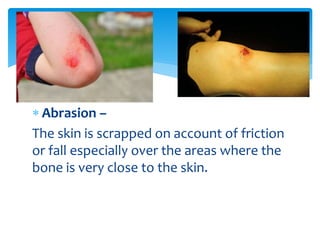
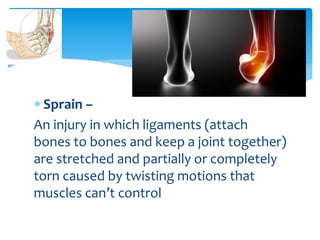
The document discusses common sports injuries, their causes, types, and basic first aid treatment. It describes how injuries can result from external violence, internal violence, or overuse. Some common types of injuries mentioned are abrasions, lacerations, contusions, strains, and sprains. It recommends RICE (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) as the standard first aid treatment for acute injuries to reduce swelling, bleeding, and pain. Chronic injuries typically develop over time from overuse rather than a single impact or event.