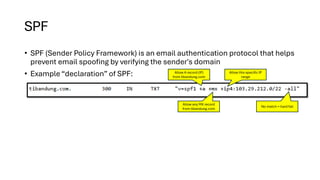
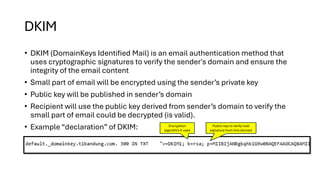
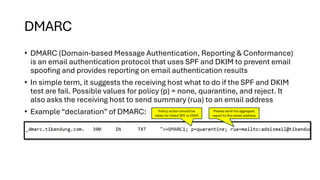
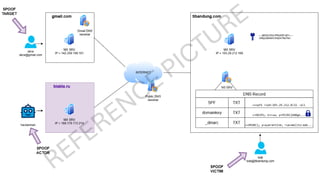
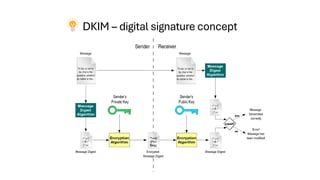
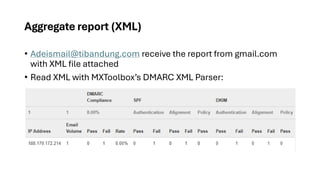
This presentation highlights key email authentication protocols—SPF, DKIM, and DMARC—to effectively combat phishing attacks. By implementing these standards, organizations can enhance email security, verify sender legitimacy, and protect users from malicious threats.