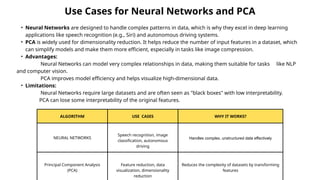
Machine learning algorithms can be broadly categorized into supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning. Supervised algorithms (like Linear Regression, Decision Trees) use labeled data for prediction, while unsupervised algorithms (like K-Means, PCA) find patterns in unlabeled data. Reinforcement learning algorithms (like Q-Learning) learn optimal actions through trial and error. Each algorithm has its strengths and weaknesses — for example, Decision Trees are simple and interpretable, while Neural Networks excel at handling complex, large datasets. The choice of algorithm depends on factors like dataset size, data complexity, training time, and the need for interpretability.