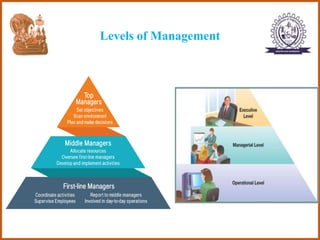
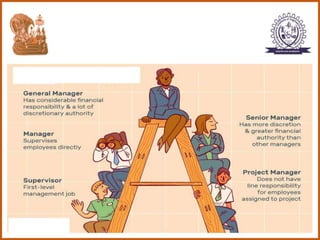
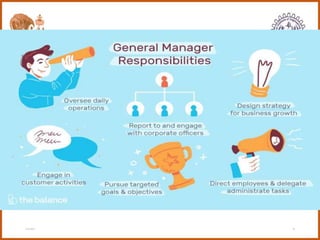
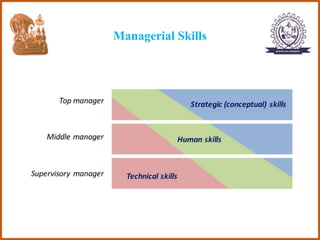
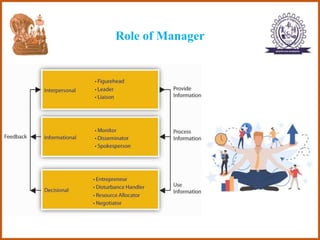
The document provides an overview of the CS8591 COMPUTER NETWORKS course, including its instructor, outcomes, and details on the first unit - Introduction and Physical Layer. Specifically, it outlines the topics that will be covered in the first unit, such as definitions of management, the evolution of management approaches, types of business organizations, and organizational culture and environment.