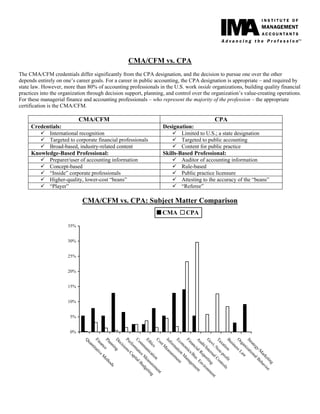
The document provides information on promoting CMA/CFM credentials. It discusses the comprehensive body of knowledge tested across areas like business analysis, management accounting, and strategic management. Earning the credentials demonstrates skills like integrating accounting into business decisions, practical experience, and commitment to ethics and excellence. The credentials mark someone as a strategic partner who can provide decision support and planning to add value to an organization. The CMA/CFM are more appropriate for corporate finance professionals, while the CPA is targeted towards public accounting.