This document summarizes a lab experiment examining the relationship between polystyrene molecular weight and thickness of spin-coated polymer films. Thin films of an unknown molecular weight polystyrene from a disposable coffee cup and a control polystyrene with a known molecular weight were created via spin coating. Film thicknesses were measured via ellipsometry to determine a linear relationship between thickness and solution concentration. This allowed extrapolation to determine the theoretical concentration needed to produce a 300 nm film for each polymer. Comparing these concentrations to established data, the molecular weights of the control and unknown polymers were estimated, though the control value fell outside acceptable error bounds.

![Marcin Kielkiewicz 108225444 CME 320 Spin Casting Lab Report Feb 25, 2015 pg 1 of 6
Abstract
The relationship between polystyrene molecular weight and thicknessof spin-coated polymer films was
examined in order to determine the unknown molecular weight of polystyrene foam from a disposable
coffee cup. Dilutesolutions of theunknownmolecularweightpolystyrene intoluenewerepreparedalong
with a control group of polystyrene pellets with a known molecular weight of 2.8*105
Da. Spin coating
andsubsequentmeasurementsof filmthicknessviaellipsometry allowedforthe graphicaldetermination
of a linearrelationshipbetweenfilmthicknessandsolutionconcentrationforboththe control groupand
the unknown. Throughextrapolationof the dataa theoretical concentrationthatwouldproduce 300 nm
thin film was determined. Comparing the theoretical concentrations to an established relationship
between molecular weight and solution concentration at 300 nm predicted the molecular weight of the
control polystyrene and the unknown extruded polystyrene foam. The molecular weight of the control
groupwasdetermined tobe 3.61*105 Da(Max: 4.87*105 Da, Min:3.46*105 Da).The unknownmolecular
weight of extrudedpolystyrene from a disposable coffee cup was determined to be 2.86*105 Da (Max:
3.29*105, Min: 2.43*105 Da). Although the molecular weight of the unknown polystyrene falls intothe
expected range the failure of our procedure to reproduce the accepted molecular weight of the control
group within the bounds of error renders our measurements of the unknown’s molecular weight
incorrect, even within the bounds of error.
Introduction
Polystyrene foam is a type of plastic
produced from the monomer styrene. It’s a
lightweight, moisture-resistant material with
exceptional insulation properties. Since it is
composedof more than90percentair,thisfoam
is also remarkably buoyant [1]
. Invented by the
Dow Chemical Company in 1941 and
trademarkedas Styrofoam™, itwasinitiallyused
by the U.S. Coast Guard and the U.S. Navy in life
rafts and preserver[2]
.The genericname for the
material isextrudedpolystyrenefoam(EPS),and
itisusedextensivelyasabuildingmaterial,inthe
packaging industry, etc. [3]
The appearance and physical properties
of various polystyrenes vary from one another
based on their intended use and method of
production. EPS is produced from styrene via a
free radical polymerization (seeFig.1) thatyields
polystyrene beads. The beads are then
subjectedto steam(orhotair) thatsustainstheir
expansionuntiltheyreachthe desireddensity.In
the final steptheEPSbeadsare senttoamolding
press. The molding process requires that the
chainlength of the polymerfallswithinaspecific
range because polystyrene with overly long
chains won't melt readily and polystyrene with
short chains will be brittle. The process is
designed to produce chains with a molecular
weight between 2.0*105
Da and 3.0*105
Da [4]
.
This study focused on determining the
average molecularweightof EPSin a disposable
coffee cup by comparing it to a sample of
polystyrene pellets (PSP) with a known
molecular weight (Mw). The Mw of the control
PSP was 2.8*105
Da, which lies withinthe range
of expected Mw distributionof the EPS. In order
to analyticallycompare the samples we created
solutions of both EPS and PSP in toluene and
fabricated a range of thins films from the
solutions through spin casting following](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e6237e5c-3caf-4c80-9ed8-03105c4eb310-151226165922/85/cm320_lab01-2-320.jpg)
![Marcin Kielkiewicz 108225444 CME 320 Spin Casting Lab Report Feb 25, 2015 pg 2 of 6
methodsinliterature[5]
.Thistechnique appliesa
centrifugal force onto a spinning substrate to
create thinfilmsonthe orderof 10-8
m to10-5
m.
Although spin casting is a well-established
experimental technique for thin film formation
the qualityof the filmproducedisthe resultof a
complex dynamic process. Vapor pressure,
solubility,viscosity,glasstransitiontemperature,
spinvelocity,andthe concentrationgradientare
some of the parametersthataffectthe thickness
of the film produced [6]
. By holding all of the
above parameters constant other than the
concentrationgradientthe relationshipbetween
polymer concentration and film thickness was
charted.
The film thickness was measured via
ellipsometrywhichhasbeensuccessfullyutilized
to determine the film thickness of thin polymer
layers with a high degree of accuracy [7]
. An
ellipsometer works by observing changes in the
state of polarizationof lightuponreflectionfrom
a surface [8]
.It isdesignedsuchthatlightreflects
firstoff a surface coated witha filmof unknown
thickness and then off a reference film with
known optical properties to determine the
thickness of the unknown layer [9]
.
To testwhetherthesurfaceof the silicon
wafers was indeed coated with a layer of
polystyrene a goniometer was used to observe
the contact angle of water on an untarnished
siliconwafervs.the contactangleonbothanEPS
coated wafer and a PSP wafer. Typically
hydrophilic substances exhibit contact angles of
lessthan90° while hydrophobicsubstanceshave
contact anglesabove 90° [10]
. Pure siliconwafers
are hydrophilic while those coated with
polystyrene are hydrophobic hence a significant
difference was expected to be observed.
To obtain the Mw of the EPS the
followingplotobtainedfromliteraturewasused
(Fig. 1) [11]
. The data in the plot derives a
correlation between the polystyrene solution
concentration and Mw of the polystyrene
necessarytofabricate athinfilmviaspincasting.
By extrapolating our plots of concentration vs.
film thickness we were able to determine the
concentration of both EPS and PSP solutions
necessary to produce a 300 nm thin film. By
comparingour theoretical concentrationtothat
predictedintheequationinFig.1we couldcheck
the reportedMw of the control PSP and findthe
unknown Mw of the EPS from the disposable
coffee cup.
Method and Materials
An EPScoffee cupfroman unknown
manufacturerwascut intosmall strips.Six
samplesfrom50 mg to 300 mg were prepared
by usinga massbalance [FIETKAUTechnology
Group INC.,ANDJewelryBalance FX-40CJ,Max:
41 g, d: 10-4
g]. The sampleswere placedinside
20 mL glassscintillationflasks and10 mL of
Figure 1. The combination of solution concentration and Mw
of polystyrene necessary to produce a 300 nm thin film.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e6237e5c-3caf-4c80-9ed8-03105c4eb310-151226165922/85/cm320_lab01-3-320.jpg)
![Marcin Kielkiewicz 108225444 CME 320 Spin Casting Lab Report Feb 25, 2015 pg 3 of 6
Toluene [Sigma Aldrich, ChromaSolv for HPLC,
>99.9%] was added to dissolve the polystyrene.
Caution was used while administering toluene
with glass Pasteur pipettes so that the toluene
did not come into contact with the latex bulb
(which could partially dissolve in toluene). The
same procedure was followed with PSP [Sigma-
Aldrich, Typical MW: 280,000 Da]. Data for the
solution concentrations obtained can be found
in Table 1.
Large Circular silicon wafers from an
unknown manufacturer were cut into 1 cm2
wafers to be used for spin casting. Two wafers
were preparedforeach sample (inordertohave
a backup in case anything went wrong). The
wafers were then positioned on the spin caster
andapproximatelythreedrops(enoughtocover
the surface of the plate) were dropped onto it.
The spin caster [Headway Research Inc., Model
PWM32] was immediatelyrunfor30 secondsat
2512 rpm. Two wafers were coated with a thin
film for each sample (total: 24 samples). A film
could be observedvisuallyonthe wafersdue to
a rainbowof colorsof the reflective surface that
varied with concentrations (similar to the effect
seen when a thin layer of
petrol is present on the
surface of water). The
samples were removed
from the spin caster with
tweezers by carefully
grabbing the edge of the
wafersandplacingthemin
a container for
safekeeping.
The film thickness
of each sample was
calculated on a Rudolph Ellipsometer AutoEl II
(error: ± 5 Å). The values of delta and psi on a
frontpanel display were reducedtothe physical
quantitiesof thicknessandrefractiveindexwhen
using the data reduction software.This was run
on a PC that was interfaced directly via the
standard RS232 serial pan [6]
. The filmthickness
of each sample was measured three times at
three differentlocationsatornear the centerof
the plate.The datacollectedisshowninTable 2.
In order to confirm the presence of a
polystyrenefilmonthe platesagoniometer[KSV
Instruments LTD, CAM 200, Optical Contact
Angle Meter] was used to compare the contact
angle of water on an untarnished silicon wafer
vs.the contact angle onbotha EPS coatedwafer
anda PSPwafer. The contactanglesobtainedare
shown in Table 3.
Results/Discussion
Data for the preparation of polymer
solutions are shown in Table 1 and the data
obtained for film thickness measurements is
shown in Table 2. From these tables the
relationshipbetweensolutionconcentrationand
Table 1. The concentration of all polystyrene solutions prepared with uncertainty calculations.
The uncertainty in mass is 0.0005 g because the mass on the balance was fluctuating without
stabilizing. V of PhCh3 stands for volume of toluene. Pi stands for solution concentration. For
the uncertainty in concentration: δpi = pi*((δm/m)2+(δV/V)2)0.5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e6237e5c-3caf-4c80-9ed8-03105c4eb310-151226165922/85/cm320_lab01-4-320.jpg)
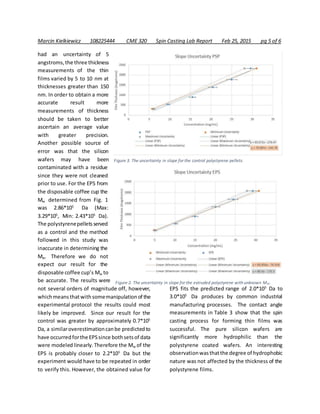
![Marcin Kielkiewicz 108225444 CME 320 Spin Casting Lab Report Feb 25, 2015 pg 4 of 6
thin film thickness is
plottedinFig.2. A linearfit
was chosen to extrapolate
the data points from both
the EPS and PSP data
points. The uncertainty for
the slope of the linear fit
was determined by finding
the minimum and
maximum slope from the
uncertainty of the data
points through methods
obtained from literature [12, 13]
. The maximum
and minimum slope for both the EPS and PSP
linear fits are shown in Fig. 3 and Fig. 4. By
extrapolatingthe datafromFig.2 andusingthe
error obtained from Fig. 3 and Fig. 4 the
concentration of PSP in toluene necessary to
deposit a thin film 300 nm
thick was estimated to be
38.8 mg/mL (Max: 39.3
mg/mL, Min: 35.2 mg/mL).
The concentrationof EPS in
solution required to
produce a film of the same
thickness was determined
via the same method, with
the concentration being
equal to 41.8 mg/mL (Max:
44.1 mg/mL, Min: 39.3
mg/mL). By comparing the
theoretical concentrations
with the plot in Fig. 1 the Mw
of both samples was
determined. The Mw of the
control PSP was3.61*105
Da (Max: 4.87*105
Da,
Min: 3.46*105
Da). From the data a result that
more closelymatchedthe Mw reportedbySigma
Aldrich was expected – approximately 2.8*105
Da. The accepted value does not lie within the
bounds of uncertainty. A likely cause of the
discrepancy is that the linear model from Fig. 2
does not predict the necessary concentration
that produces300 nm thinfilm. Anothersource
of error may have been our measurements of
thin film thickness. Although the ellipsometer
Table 2. Three thickness measurements of each thin film coated silicon wafer. Avg. stands for
average thickness. For the uncertainty in the average thickness:
δAvg. = ((δTh1)2+(δTh2)2+(δTh3)2)0.5
Figure 2. A plot of polystyrene solution in concentration vs. the film thickness produced
through spin casting for both extruded polystyrene and the control polystyrene pellets. A
linear fit for both data were obtained.
Table 3. Contact angle of water droplets on pure silicon wafers and
polystyrene coated silicon wafers.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e6237e5c-3caf-4c80-9ed8-03105c4eb310-151226165922/85/cm320_lab01-5-320.jpg)
![Marcin Kielkiewicz 108225444 CME 320 Spin Casting Lab Report Feb 25, 2015 pg 6 of 6
Conclusion
Polystyrene solutions in toluene were
successfullyspincastontosiliconwafersinorder
to determine a relationship between polymer
concentrationinsolutionandthinfilmthickness.
Through the extrapolation of data a theoretical
concentration that would result in 300 nm thin
film was predicted. Comparing the theoretical
concentrations to an established relationship
between molecular weight and solution
concentration at 300 nm gave results for the
molecular weight of the control polystyrene as
well as the molecular weight of the extruded
polystyrenefoam. The molecular weight of the
control groupwasdeterminedtobe 3.61*105
Da
(Max: 4.87*105
Da, Min: 3.46*105
Da). The
accepted value was 2.8*105
Da. The unknown
molecular weight of the extruded polystyrene
froma disposable coffeecupwasdeterminedto
be 2.86*105
Da (Max: 3.29*105
, Min: 2.43*105
Da). Although the molecular weight of the
unknown polystyrene falls into the expected
range the failure of our procedure to reproduce
the accepted molecular weight of the control
group within the bounds of error renders our
measurements of the unknown molecular
weight incorrect, even within the bounds of
error.
References
[1] Maier,Karyn, and Bronwyn Harris."WhatIs
Polystyrene Foam?" WiseGeek. Conjecture.
[2] "Invention of STYROFOAM™." Dow. Building
Solutions. Dow Chemical Company.
[3] Flynn, Hillary,and Bronwyn Harris."WhatAre the
Different Uses of Polystyrene?" WiseGeek.
Conjecture.
[4] Secrest, Rose. "Expanded Polystyrene
Foam." How Products Are Made. Advameg, Inc.
[5] D.W.Schubert. Spin Coating as a Method for
Molecular Weight Determination. Polymer Bulletin,
2007. Vol. 38,Issue2, pg 177-184
[6] Ennis,David,Heike Betz, and Harald Ade. "Direct
Spin casting of Polystyrene Thin Films onto
Poly(methyl Methacrylate)." Journal of Polymer
Science Part B: Polymer Physics 44.22 (2006): 3234-
244.
[7] Fujiwara,Hiroyuki."Spectroscopic Ellipsometry:
Principles and Applications."GoogleBooks. 2007
[8] "Rudolph AutoEL II." Rudolph Ellipsometer AutoEL
II.
[9] Goncalves,Debora. "Fundamentals and
Applications of Spectroscopic Ellipsometry." Química
Nova.
[10] Trotter, Brian,Garret Moddel, Rachel Ostroff,
and Gregory R. Bogart. "Fixed-polarizer Ellipsometry:
A SimpleTechnique to Measure the Thickness of
Very Thin Films." Optical Engineering 38.5 (1999):
902. Electrical and Computer Engineering
Dept. University of Colorado.
[11] Renate Förch, Holger Schönherr, A. Tobias A.
Jenkins (2009).Surface design: applications in
bioscience and nanotechnology. Wiley-VCH. p. 471.
[12] "Slope Uncertainty." Introductory Physics Lab.
[13] Sheehan, Michael."Uncertainty in Slope of
Trendline." YouTube.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/e6237e5c-3caf-4c80-9ed8-03105c4eb310-151226165922/85/cm320_lab01-7-320.jpg)
