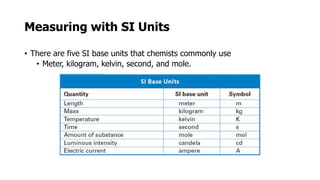
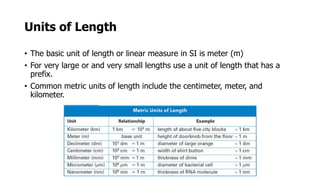
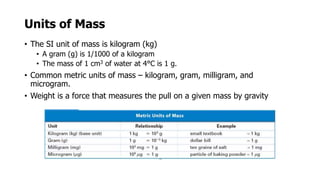
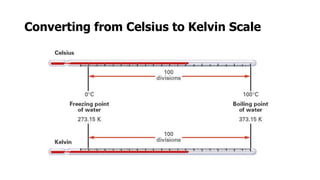
Clinical chemistry involves the biochemical analysis of body fluids to aid in disease diagnosis and treatment. It utilizes chemical reactions to measure levels of compounds in fluids like blood and urine. This provides information to help diagnose and monitor various diseases. Some key diseases diagnosed using clinical chemistry tests include cardiac failure, liver diseases, cancer, renal failure, and hormone imbalances. Common tests measure components like blood glucose, electrolytes, enzymes, lipids, and hormones. The results of these tests can provide indications of metabolic disorders and organ damage. Clinical chemistry relies on standardized metric units and methods like colorimetry, spectrophotometry, and immunoassays to precisely measure target analytes in patient samples.