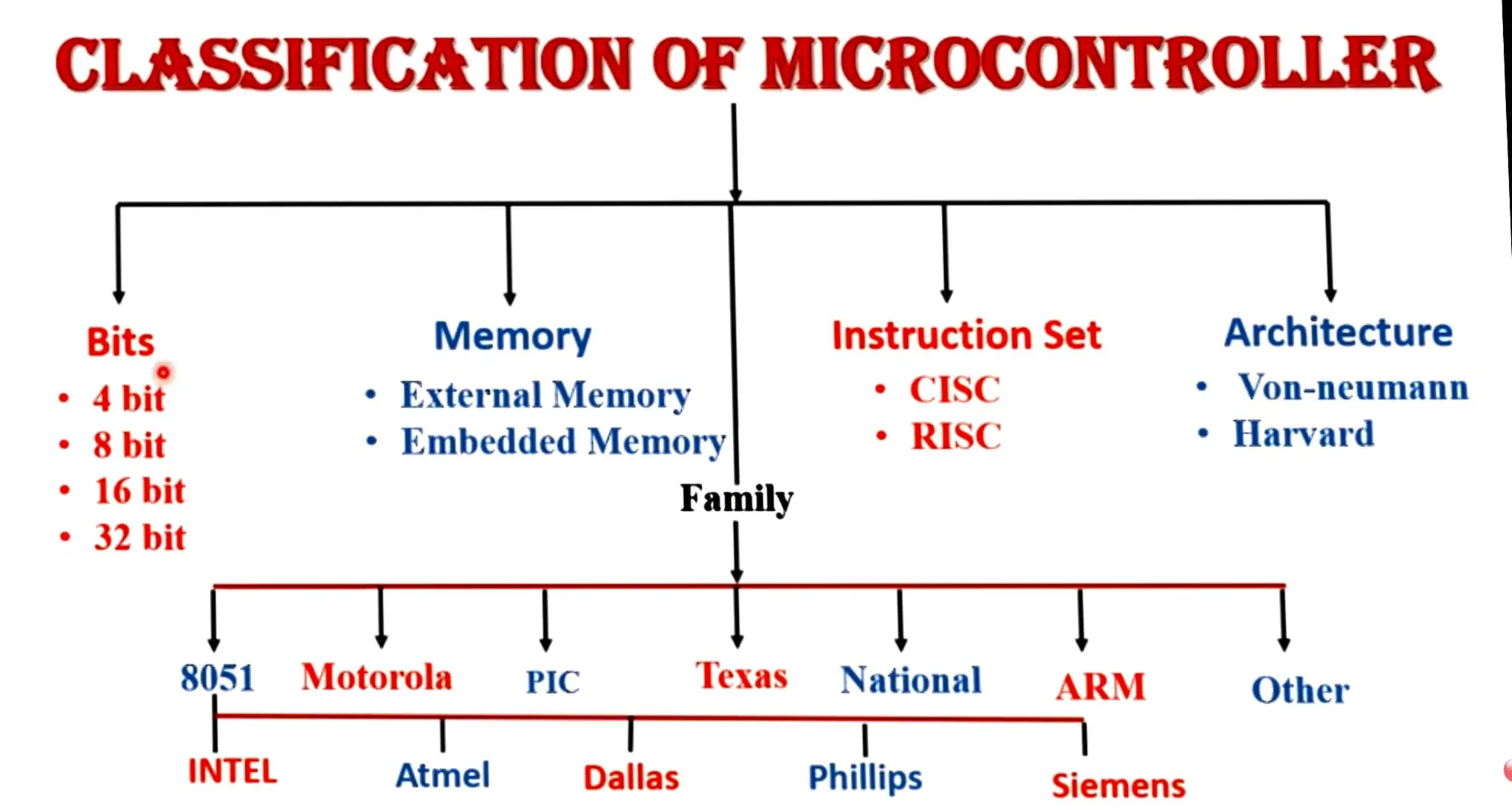
The document provides a block diagram and overview of the components and classifications of microcontrollers. It shows that a microcontroller contains an ALU, registers, RAM, ROM, CPU, interrupt circuit, timer/counter, program counter, stack pointer, clock circuit, and input/output ports. It then classifies microcontrollers based on bits, memory, instruction set, architecture, family, and according to memory devices.
![Block Diagram of Microcontroller
ALU
(ArithmeHc Logic Unit)
Registers
(Accumulator &
General Purpose)
I RAM
I ROM
[ CPU
Interrupt
Circuit
Timer / Counter
I
I
]
0
Program Counter
(PC)
Stack Pointer
(SP)
Clock
Circuit
Input / Output Ports](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/classificationofmicrocontroller8051-231225125245-31ca51ec/75/classification-of-microcontroller-8051-pdf-1-2048.jpg)