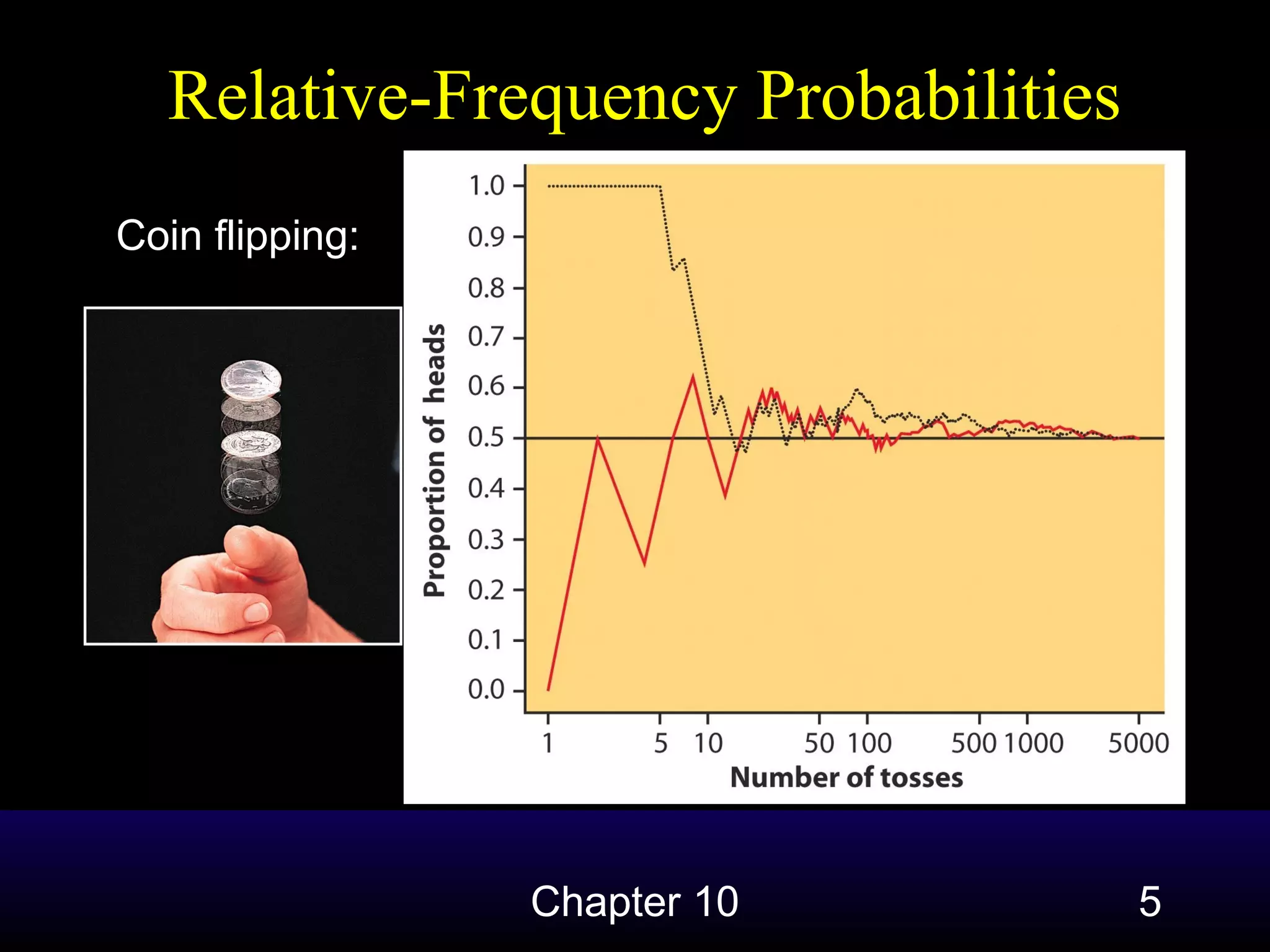
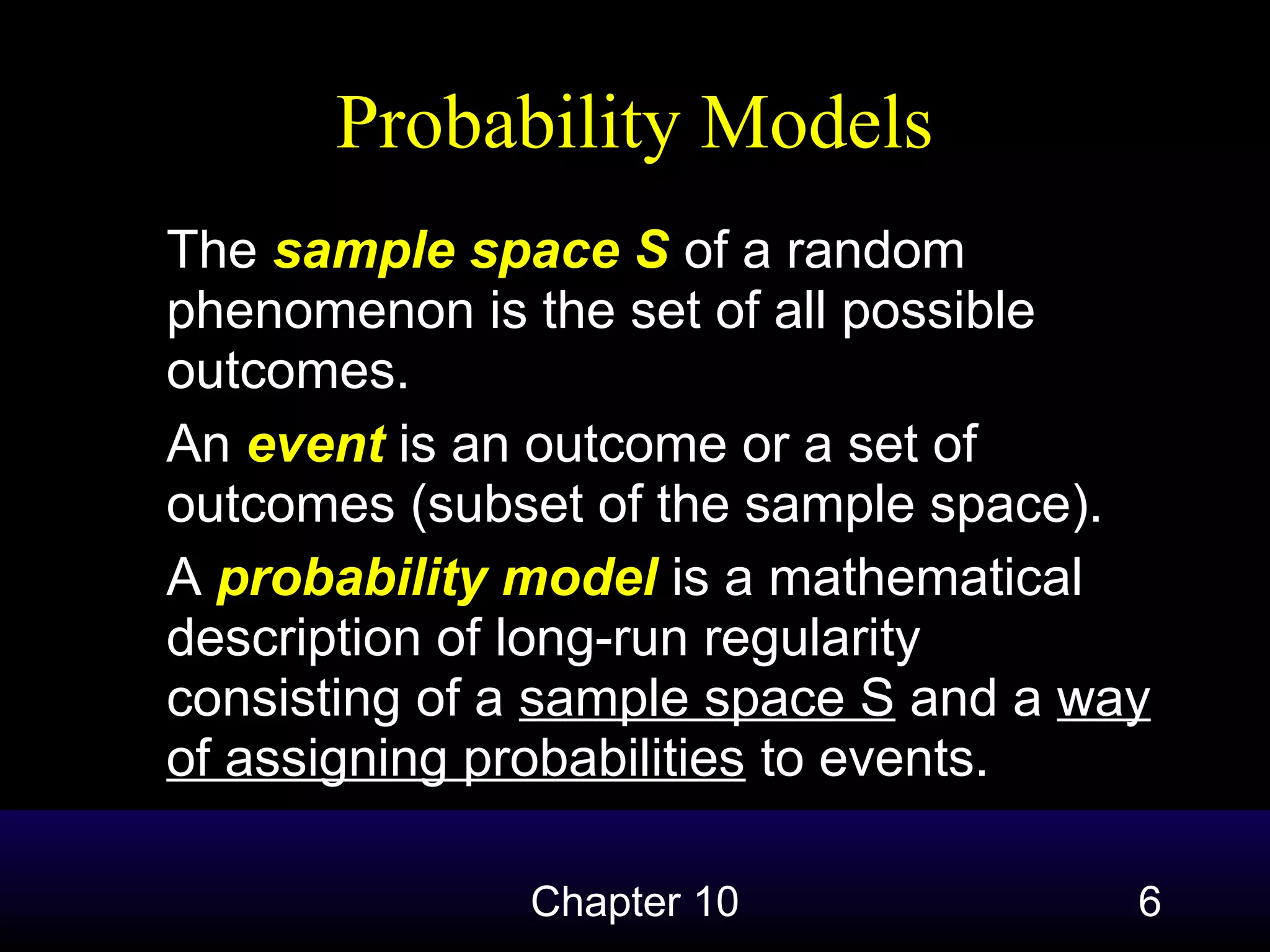
This document introduces the concept of probability and some basic probability rules. It defines probability as describing the long-run behavior of random events, where individual outcomes are unpredictable in the short-run but follow regular patterns over many repetitions. Probability is quantified using relative frequencies of outcomes in large samples or simulations. A probability model defines a sample space containing all possible outcomes of a random phenomenon and assigns probabilities to events within that space. The document outlines four basic probability rules: 1) probabilities are between 0 and 1, 2) the probabilities of all outcomes must sum to 1, 3) the probability of mutually exclusive events is the sum of their individual probabilities, and 4) the probability of an event not occurring is 1 minus the probability of it occurring