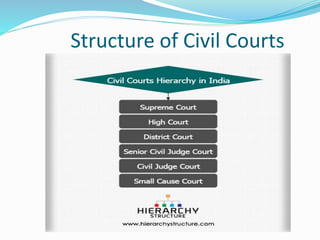
The Civil Procedure Code establishes the procedures and laws regarding civil matters in India. It consolidates and amends the law relating to civil procedure and practices in civil courts. The CPC consists of two parts - Part 1 contains 158 sections establishing jurisdiction, while Part 2 contains schedules outlining rules and orders. The CPC creates different types of jurisdiction for civil courts, including jurisdiction over subject matter, territory, persons, and monetary limits. It also establishes procedures for appeals, references, reviews, and revisions of civil court rulings.