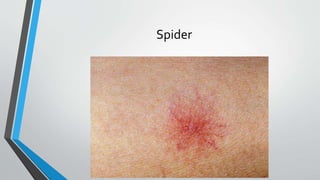
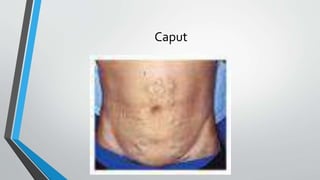
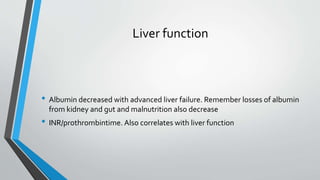
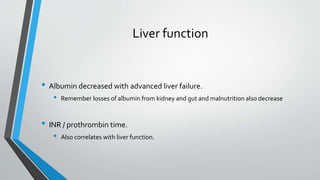
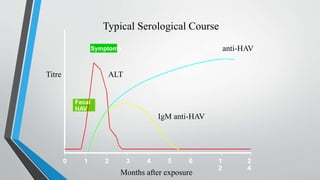
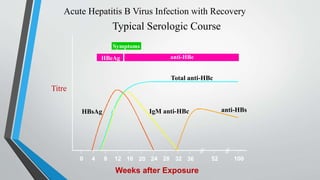
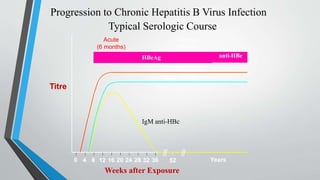
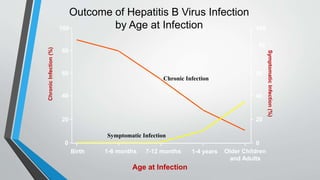
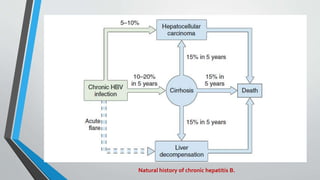
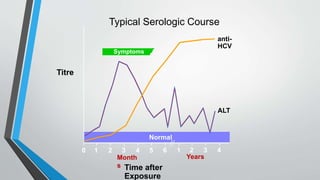
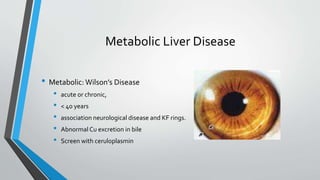
This document provides an overview of the approach to chronic liver disease. It discusses the history, physical exam findings, and abnormal liver chemistry patterns seen in various liver diseases. It then describes the characteristics of hepatocellular and cholestatic liver injury. Specific liver diseases covered include viral hepatitis A, B, C, alcoholic liver disease, drug/toxic hepatitis, autoimmune hepatitis, and metabolic/cholestatic liver diseases. Testing and clinical course are outlined for each condition.