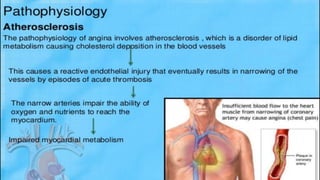
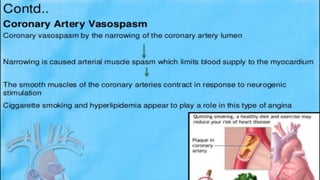
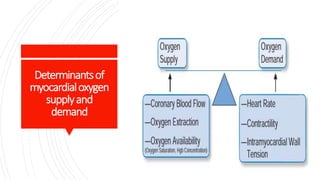
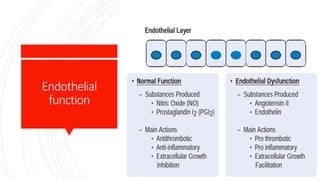
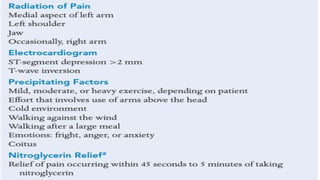
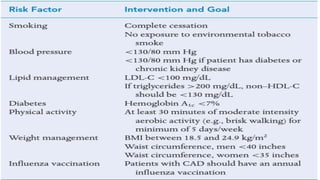
This document discusses chronic stable angina, including its definition, causes, diagnosis, goals of treatment, and treatment options. It defines chronic stable angina as chest pain or discomfort caused by insufficient blood flow to the heart muscle during physical exertion or emotional stress. The major determinants of insufficient flow are described as heart rate, contractility, and intramyocardial wall tension. Diagnosis involves electrocardiograms and stress tests, while treatment goals are to reduce symptoms and prevent complications through lifestyle changes, medications, and procedures. Common medications discussed are antiplatelet drugs, beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, nitrates, ACE inhibitors, statins, and newer options like ranolazine and ivabrad