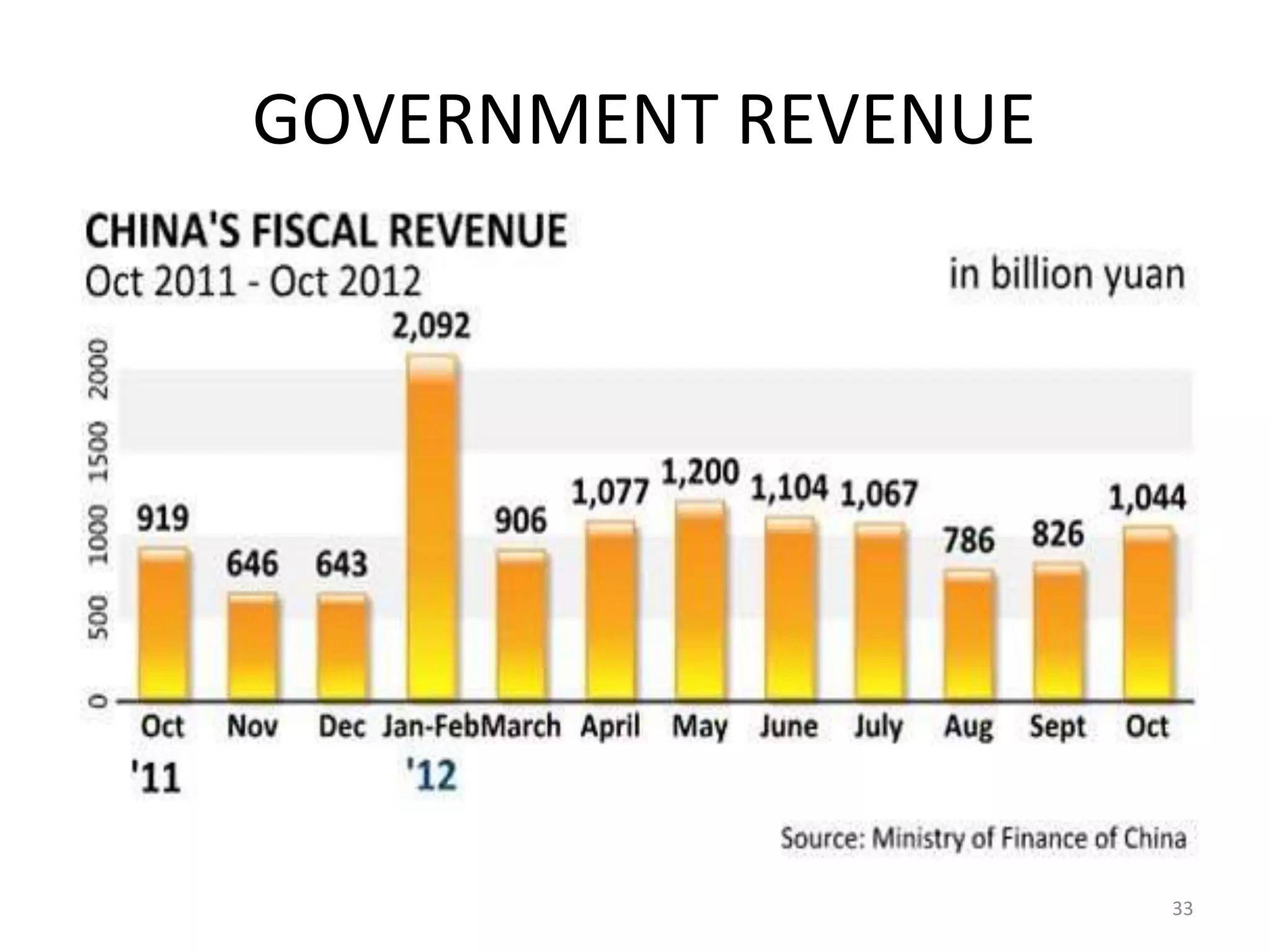
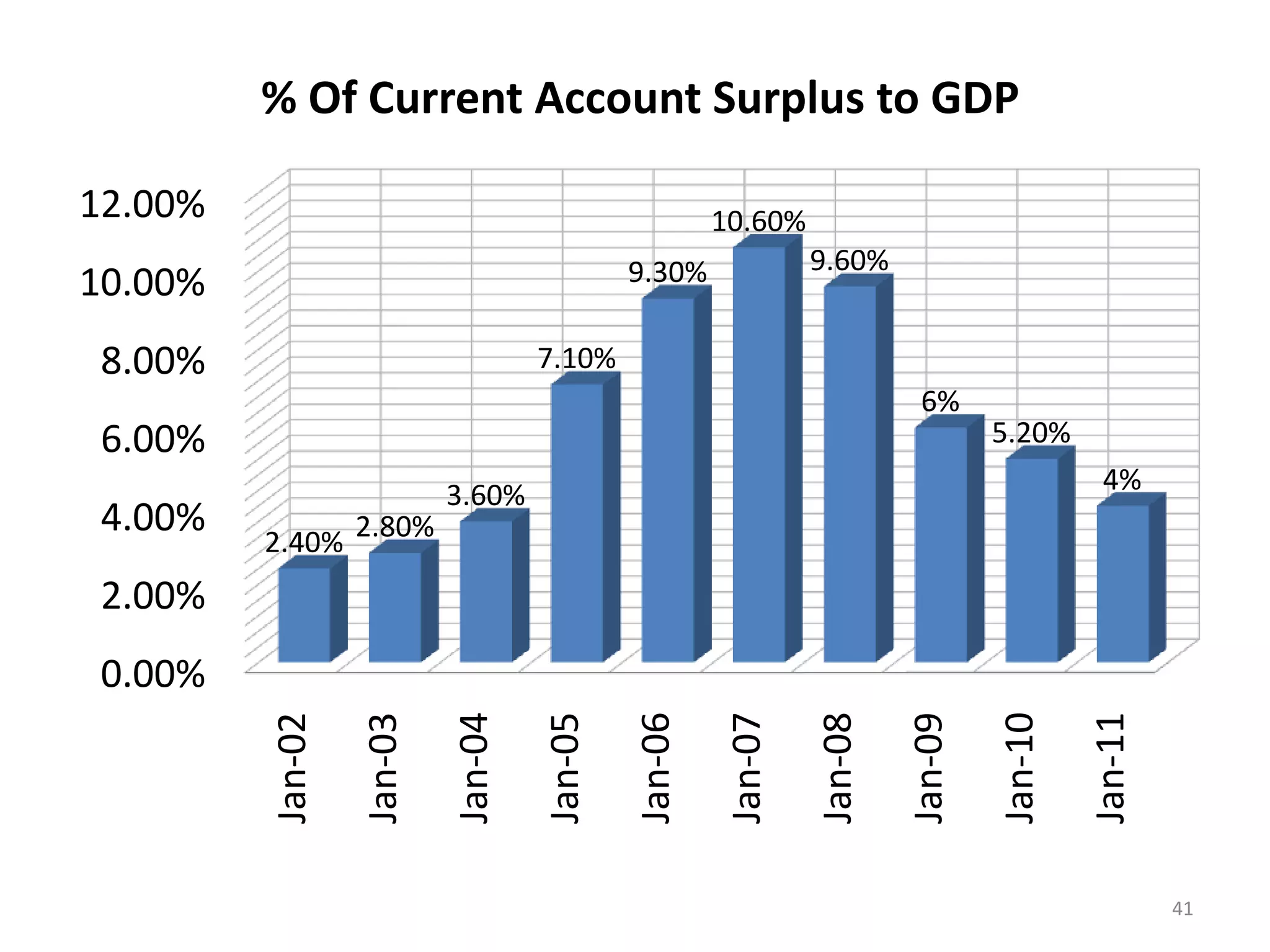
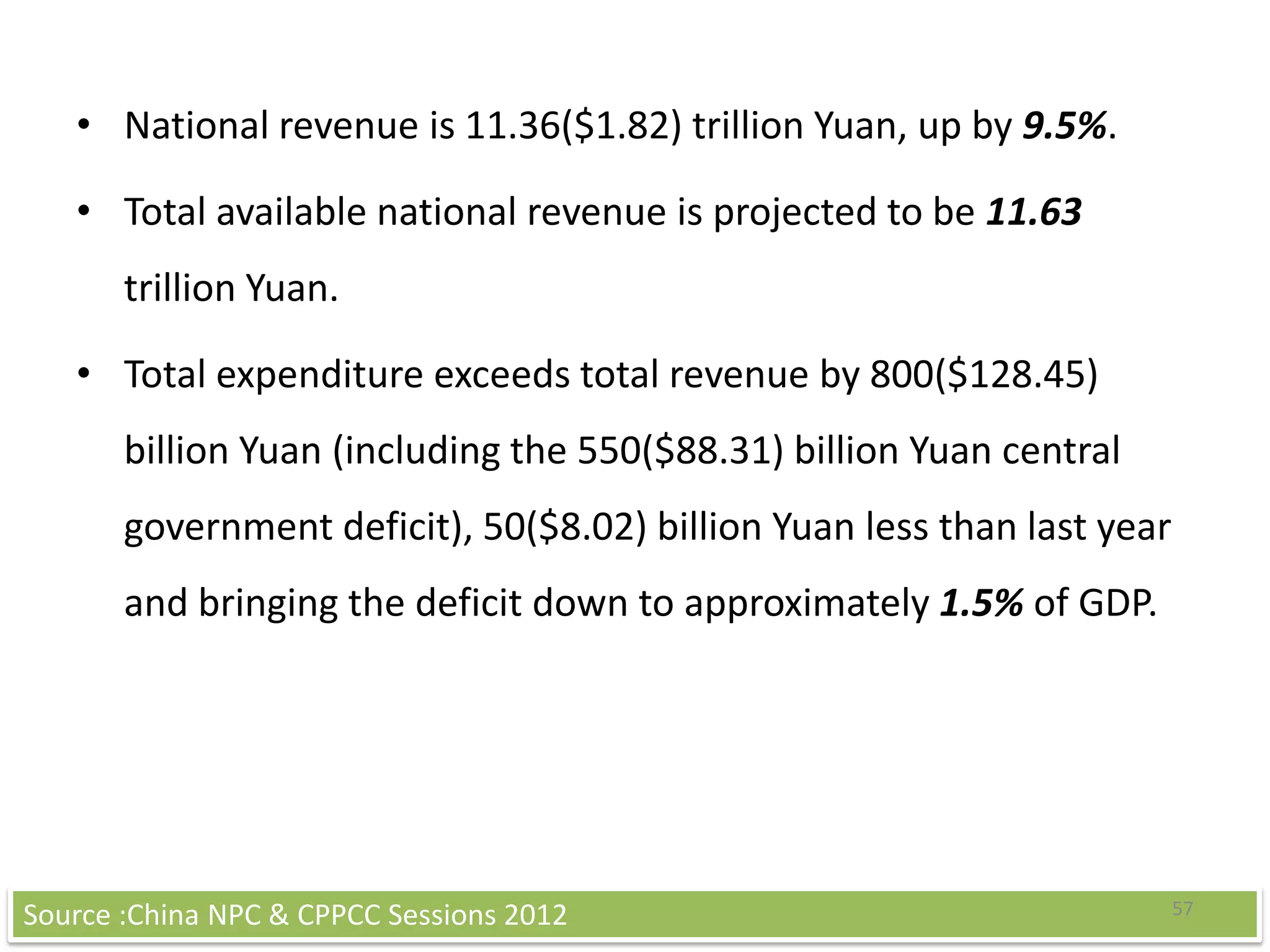
China's GDP grew by 7.4% in the third quarter of 2012, representing a sharp slowdown from previous years. Growth has fallen below the target range of 9-10% due to factors such as falling exports and imports, a decline in industrial output, a collapse in real estate investment, and falling consumer prices. Unemployment remains low at 4.1% as China focuses on job creation. China runs a current account surplus equivalent to around 4% of its GDP and has large foreign exchange reserves of over $3 trillion. The government is focusing fiscal policy on tax cuts and spending on education, healthcare and social programs to boost domestic consumption.