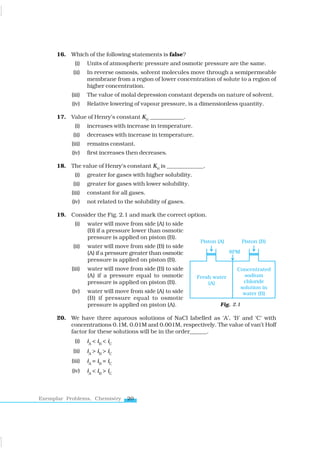
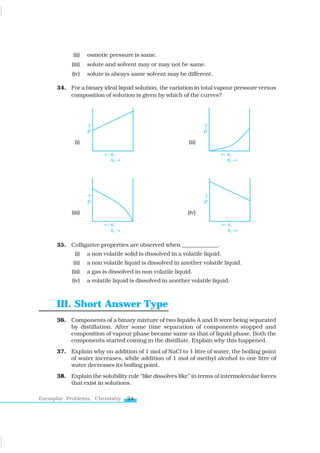
The document contains multiple-choice questions and short answer prompts focused on concepts of solution chemistry, including factors affecting solubility, colligative properties, and the behavior of mixtures under varying conditions. It addresses topics such as Raoult’s law, osmotic pressure, and the significance of Henry's law, while testing knowledge on the interaction of solutes and solvents. Additionally, it includes matching type questions to correlate various terms related to solutions.