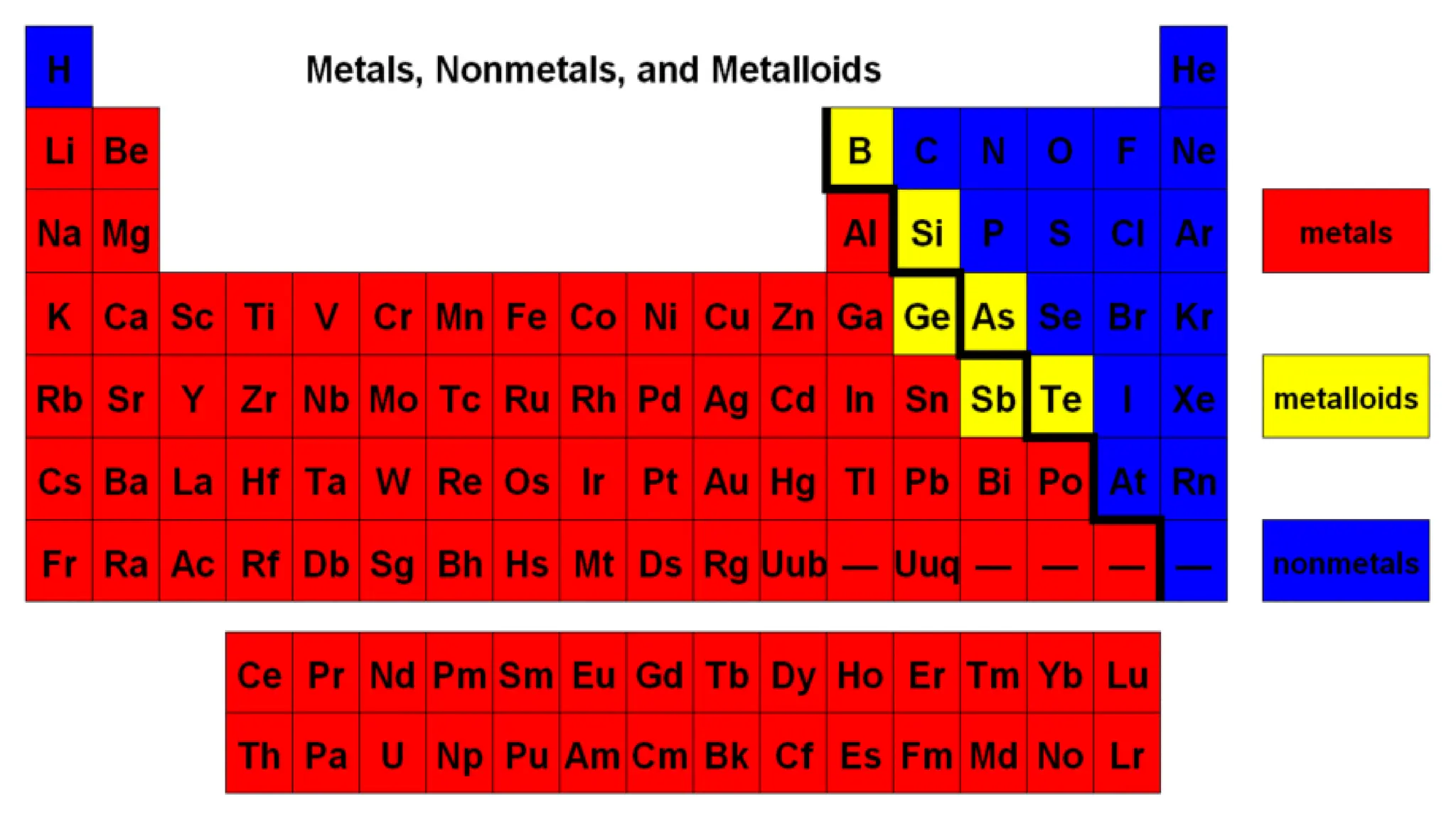
The document provides an overview of chemical bonding, categorizing elements into metals, non-metals, and metalloids, and detailing chemical compounds, including ionic and covalent types. Ionic compounds form from the transfer of electrons from metals to nonmetals, while covalent compounds arise from the sharing of electrons among nonmetals, each exhibiting distinct properties such as melting points and solubility. The document also includes examples of various compounds and comparisons between the properties of ionic and covalent compounds.