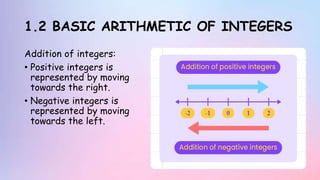
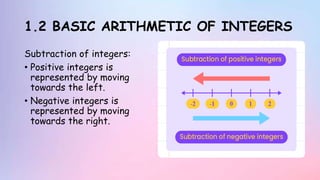
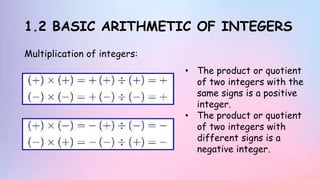
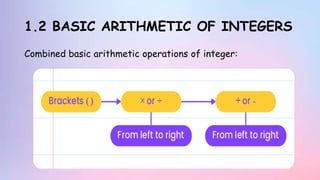
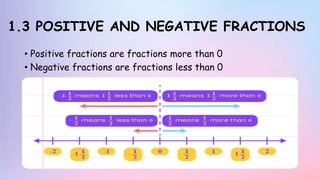
The document provides information about rational numbers including integers, fractions, decimals, and rational numbers. It defines positive and negative integers, fractions, and decimals. It discusses the basic arithmetic operations of adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing rational numbers. It provides examples of problems and exercises involving operations on rational numbers. The document is a chapter from a textbook on rational numbers intended to teach students about the different types of rational numbers and how to perform calculations with them.