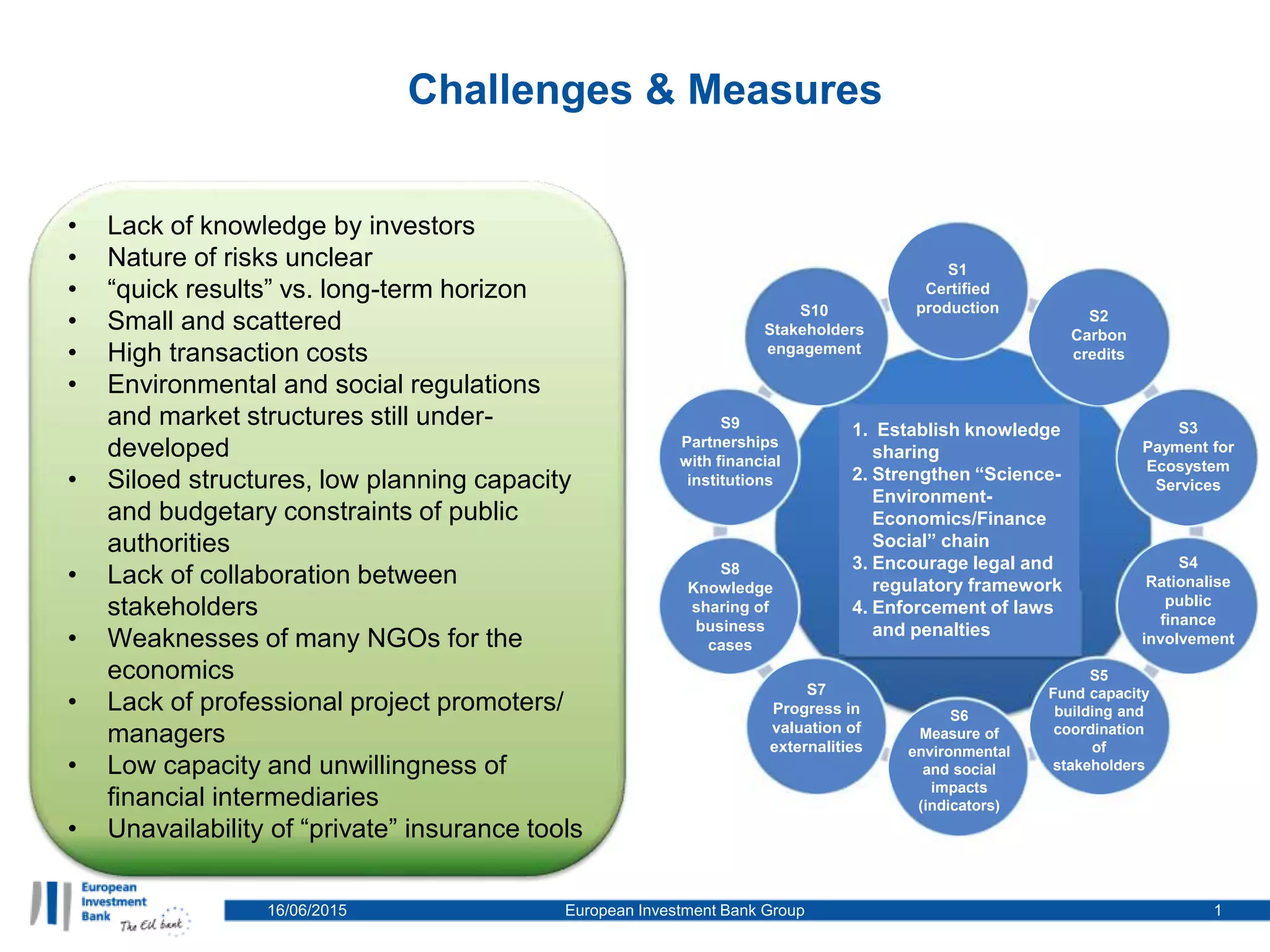
The document identifies challenges in investment related to environmental and social projects, highlighting issues such as investor knowledge gaps, unclear risks, and high transaction costs. It proposes measures to improve collaboration, strengthen legal frameworks, and enhance knowledge sharing among stakeholders. Recommendations include establishing partnerships with financial institutions and developing better methods to measure environmental and social impacts.