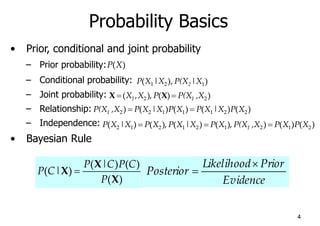
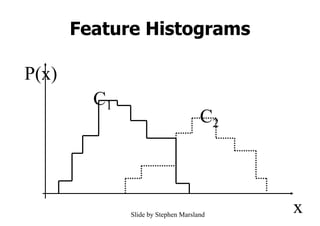
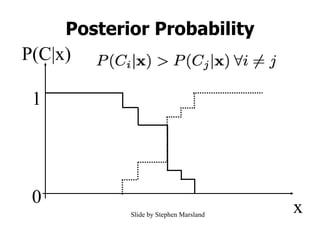
Naïve Bayes is a probabilistic classifier that applies Bayes' theorem with a strong (naive) independence assumption. It estimates the probability of a class given an instance by calculating the product of the prior probability of the class and the conditional probability of each attribute value given the class. This allows easy and fast training by separately estimating attribute probabilities in each class from training data. Classification is done by looking up these probabilities to find the class with the highest posterior probability for a new instance. Naïve Bayes works surprisingly well in practice despite its independence assumption often being violated.



![11
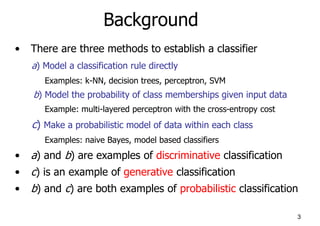
Naïve Bayes
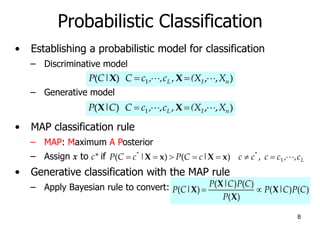
• Bayes classification
Difficulty: learning the joint probability
• Naïve Bayes classification
– Making the assumption that all input attributes are independent
– MAP classification rule
)
(
)
|
,
,
(
)
(
)
(
)
( 1 C
P
C
X
X
P
C
P
C
|
P
|
C
P n
X
X
)
|
,
,
( 1 C
X
X
P n
)
|
(
)
|
(
)
|
(
)
|
,
,
(
)
|
(
)
|
,
,
(
)
;
,
,
|
(
)
|
,
,
,
(
2
1
2
1
2
2
1
2
1
C
X
P
C
X
P
C
X
P
C
X
X
P
C
X
P
C
X
X
P
C
X
X
X
P
C
X
X
X
P
n
n
n
n
n
L
n
n c
c
c
c
c
c
P
c
x
P
c
x
P
c
P
c
x
P
c
x
P ,
,
,
),
(
)]
|
(
)
|
(
[
)
(
)]
|
(
)
|
(
[ 1
*
1
*
*
*
1
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch8bayes-230216134338-1ca0201a/85/ch8Bayes-ppt-11-320.jpg)
![12
Naïve Bayes
• Naïve Bayes Algorithm (for discrete input attributes)
– Learning Phase: Given a training set S,
Output: conditional probability tables; for elements
– Test Phase: Given an unknown instance ,
Look up tables to assign the label c* to X’ if
;
in
examples
with
)
|
(
estimate
)
|
(
ˆ
)
,
1
;
,
,
1
(
attribute
each
of
value
attribute
every
For
;
in
examples
with
)
(
estimate
)
(
ˆ
of
value
target
each
For 1
S
S
i
jk
j
i
jk
j
j
j
jk
i
i
L
i
i
c
C
a
X
P
c
C
a
X
P
N
,
k
n
j
x
a
c
C
P
c
C
P
)
c
,
,
c
(c
c
L
n
n c
c
c
c
c
c
P
c
a
P
c
a
P
c
P
c
a
P
c
a
P ,
,
,
),
(
ˆ
)]
|
(
ˆ
)
|
(
ˆ
[
)
(
ˆ
)]
|
(
ˆ
)
|
(
ˆ
[ 1
*
1
*
*
*
1
)
,
,
( 1 n
a
a
X
L
N
x j
j
,](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch8bayes-230216134338-1ca0201a/85/ch8Bayes-ppt-12-320.jpg)
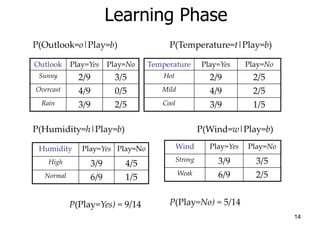
![15
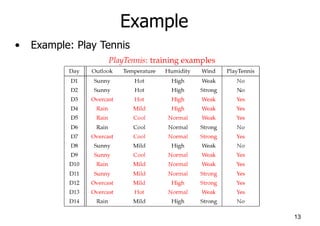
Example
• Test Phase
– Given a new instance,
x’=(Outlook=Sunny, Temperature=Cool, Humidity=High, Wind=Strong)
– Look up tables
– MAP rule
P(Outlook=Sunny|Play=No) = 3/5
P(Temperature=Cool|Play==No) = 1/5
P(Huminity=High|Play=No) = 4/5
P(Wind=Strong|Play=No) = 3/5
P(Play=No) = 5/14
P(Outlook=Sunny|Play=Yes) = 2/9
P(Temperature=Cool|Play=Yes) = 3/9
P(Huminity=High|Play=Yes) = 3/9
P(Wind=Strong|Play=Yes) = 3/9
P(Play=Yes) = 9/14
P(Yes|x’): [P(Sunny|Yes)P(Cool|Yes)P(High|Yes)P(Strong|Yes)]P(Play=Yes) = 0.0053
P(No|x’): [P(Sunny|No) P(Cool|No)P(High|No)P(Strong|No)]P(Play=No) = 0.0206
Given the fact P(Yes|x’) < P(No|x’), we label x’ to be “No”.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch8bayes-230216134338-1ca0201a/85/ch8Bayes-ppt-15-320.jpg)



