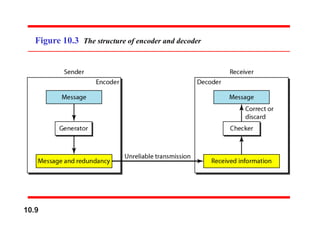
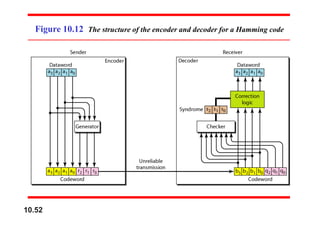
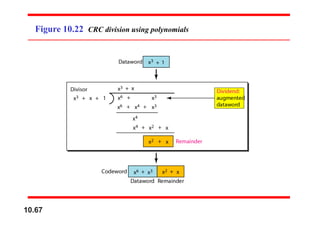
This document discusses error detection and correction in digital communications. It introduces block coding where messages are divided into blocks of k bits with r redundant bits added to each block, making the block length n=k+r. Linear block codes are discussed where the XOR of two codewords results in a third valid codeword. The minimum Hamming distance dmin relates to the error detection and correction capabilities of a code, with dmin=s+1 needed to detect s errors and dmin=2t+1 to correct t errors. Examples are given of simple parity-check codes and generating codewords from datawords.