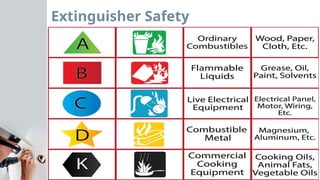
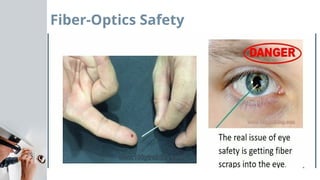
Chapter 1 covers cabling and safety practices within the telecommunications industry, emphasizing the importance of standardized installation for quality connections. It discusses various cabling methods, safety codes, and the potential dangers associated with electrical work, including appropriate safety gear and protocols. Additionally, it outlines the significance of a proper work environment and adherence to safety regulations to prevent accidents and ensure overall security.