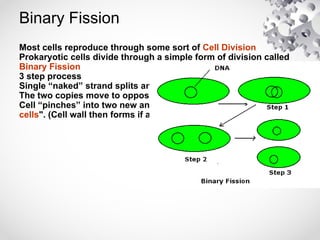
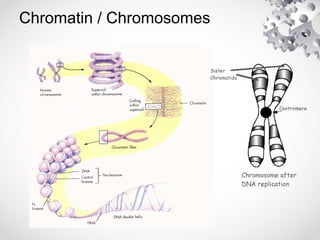
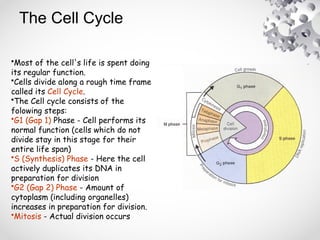
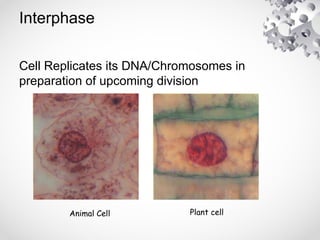
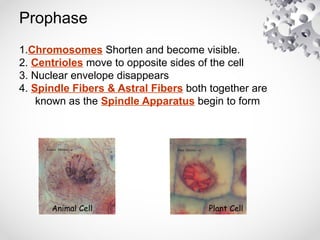
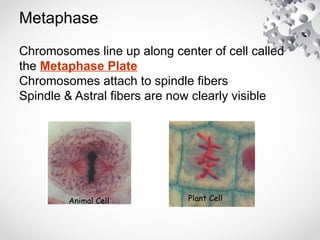
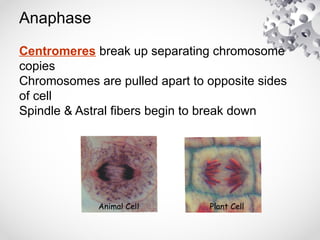
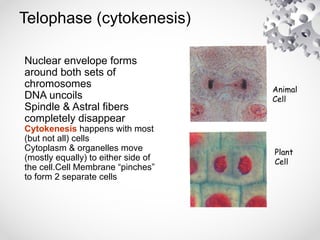
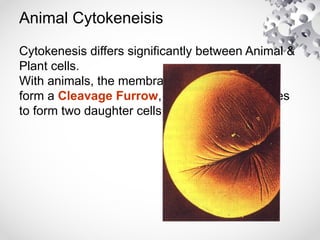
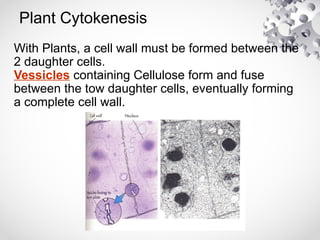
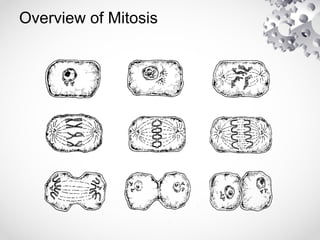
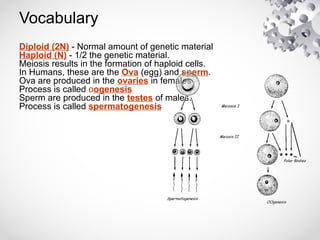
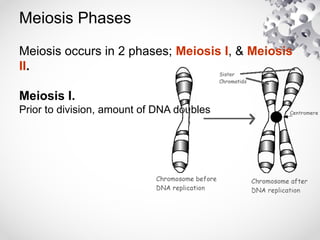
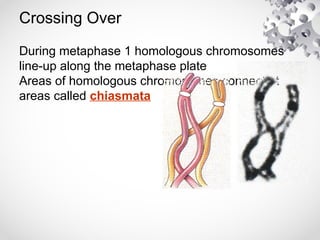
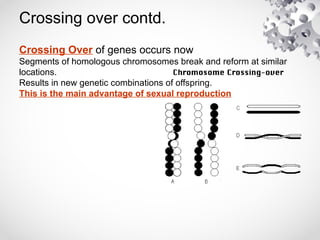
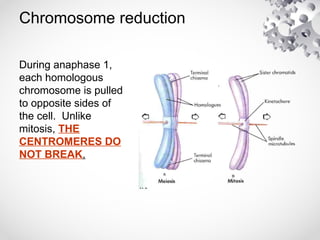
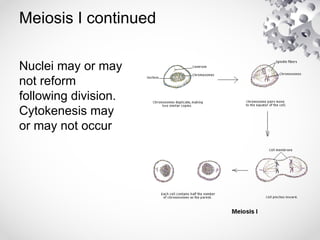
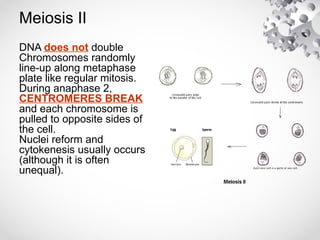
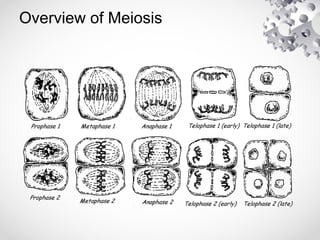
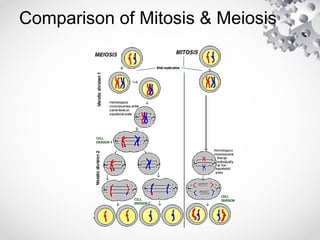
The document outlines the processes of cell division including binary fission, mitosis, and meiosis. It describes the steps in the cell cycle, the detailed phases of mitosis including prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase, as well as the differences in cytokinesis in animal and plant cells. Additionally, it explains meiosis, its phases, and the significance of genetic variation through processes like crossing over.