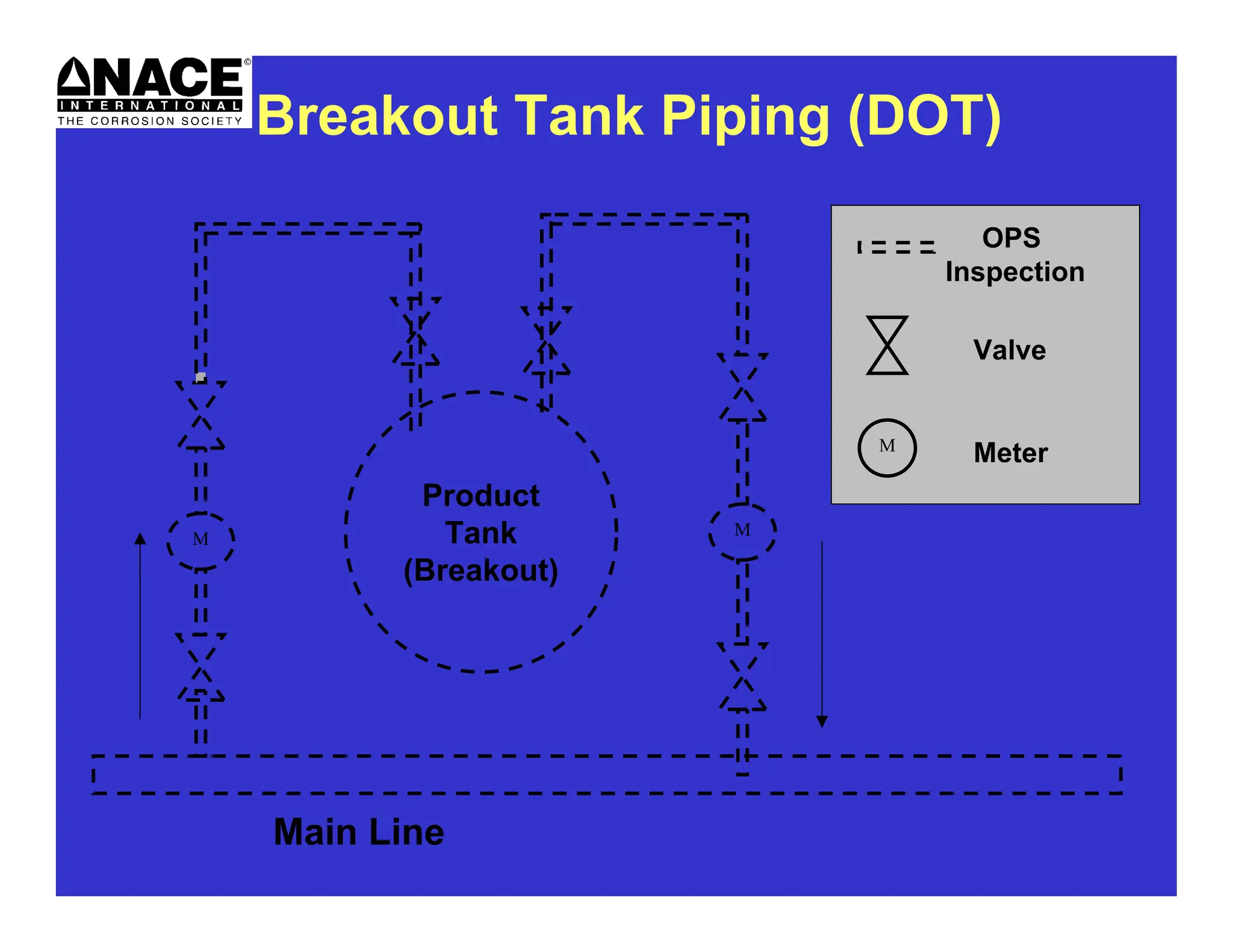
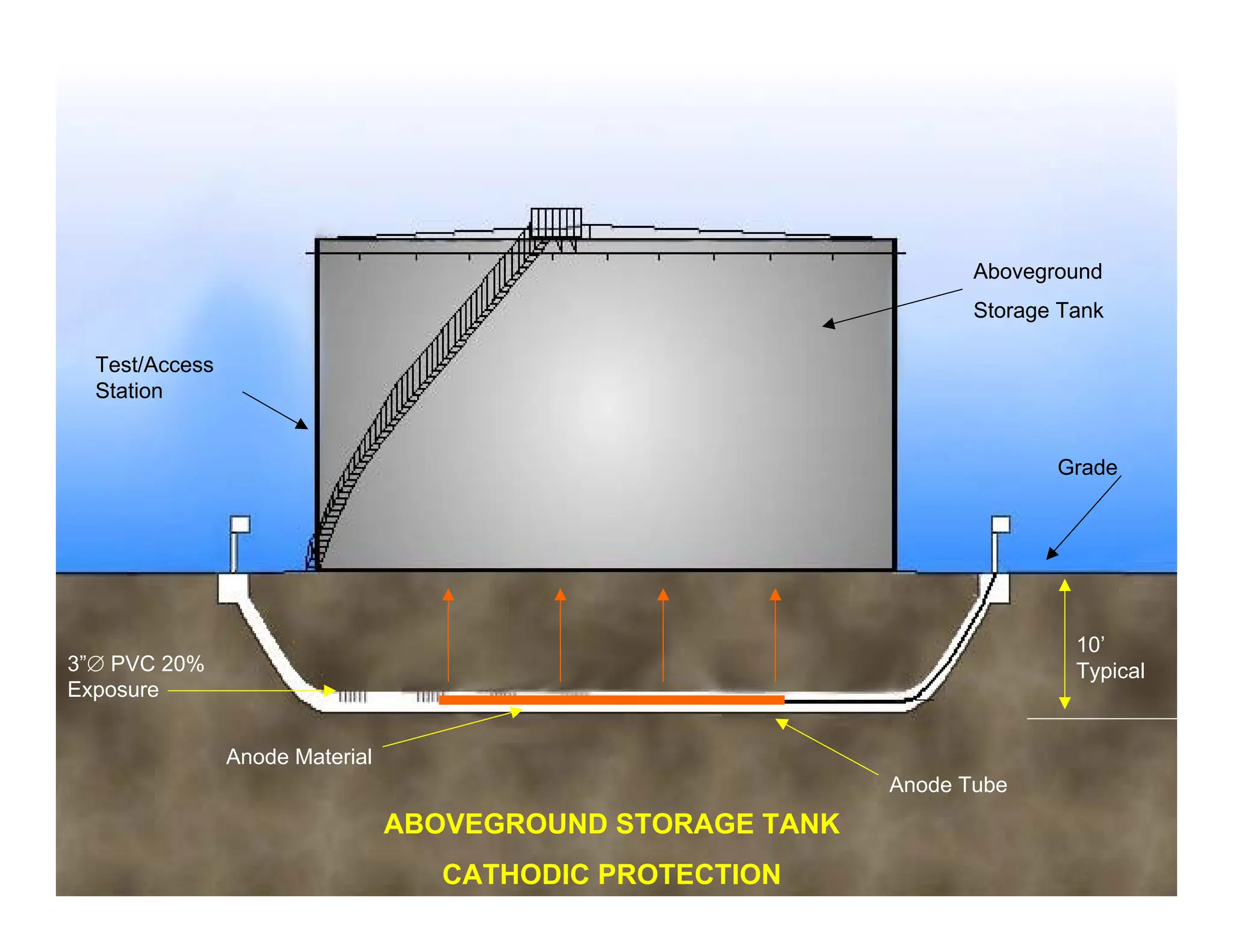
The document covers the importance of cathodic protection for on-grade storage tanks and buried piping, discussing corrosion causes, government regulations, and maintenance requirements. It highlights that approximately 25% of states require cathodic protection for new or refurbished tanks to prevent corrosion and ensure compliance with SPCC regulations. Key elements involve anode and cathode functions, galvanic protection systems, and maintenance practices to minimize environmental impact and liability.