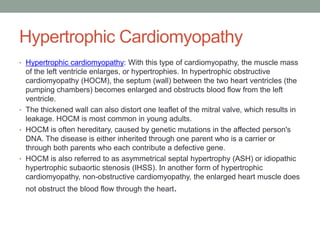
Cardiomyopathy is a chronic heart muscle disease that leads to impaired blood pumping and can result in arrhythmias and heart failure. There are four main types: dilated, hypertrophic, restrictive, and arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy, each with distinct causes and characteristics. Diagnosis involves imaging and electrical tests, while treatment options include medications, lifestyle changes, and in severe cases, surgery.