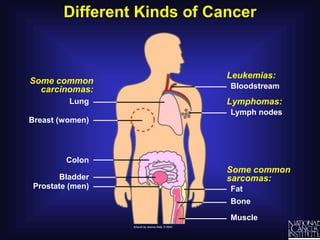
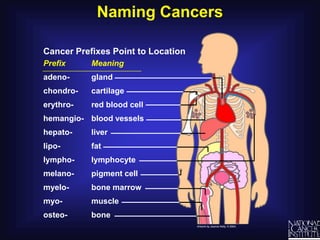
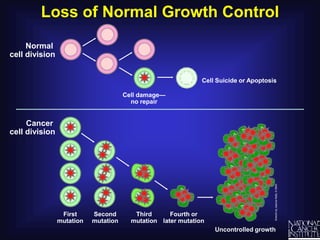
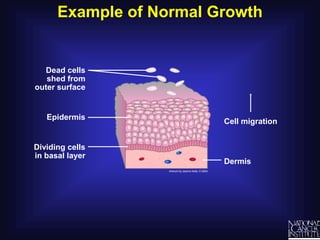
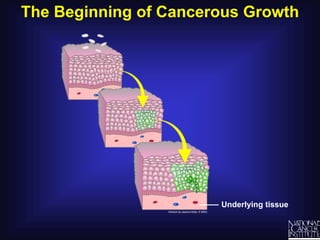
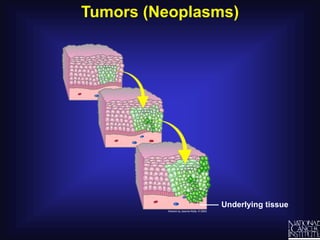
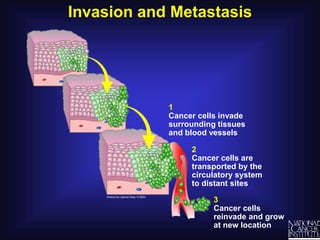
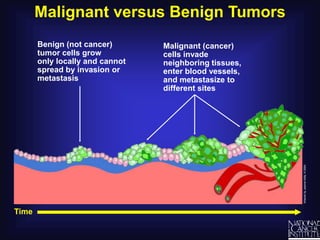
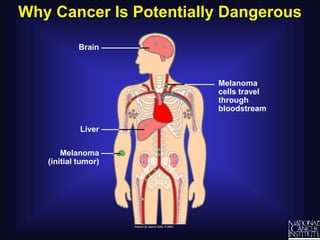
Cancer is caused by uncontrolled cell growth. The document discusses what cancer is, different types like carcinomas and sarcomas, how cancers are named by their location, the role of genes in cancer development, and the multi-step process of normal cells becoming cancerous cells that can invade nearby tissues and spread via the bloodstream to other parts of the body (metastasis). Malignant tumors are cancerous, while benign tumors only grow locally and do not metastasize.