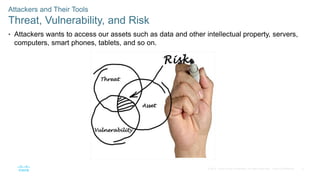
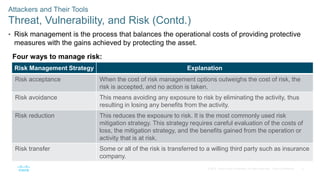
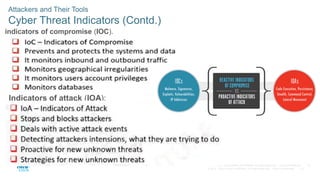
The document discusses attackers and their tools. It defines key cybersecurity terms like threats, vulnerabilities, risks and explains how risks are managed. It describes different types of attackers like hackers, cybercriminals and state-sponsored actors. It also discusses the tools used by attackers, how they have evolved over time, and categories of common network attacks. The goal is to understand the landscape of attackers and tools in order to better defend networks and assets.