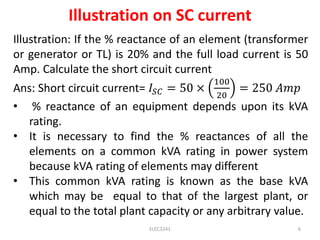
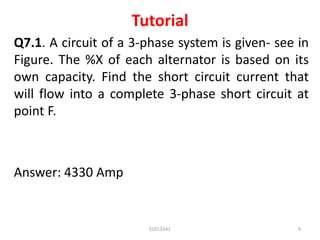
This document discusses symmetrical faults in power systems. It defines a symmetrical fault as one that results in equal fault currents in lines with 120 degree displacement. Symmetrical faults are rare but the most severe as they impose heavy duties on circuit breakers. The percentage reactance, base kVA, short circuit current, and steps for calculating symmetrical fault currents are explained. Several examples are provided to illustrate how to calculate short circuit current and kVA at different points in a power system network.