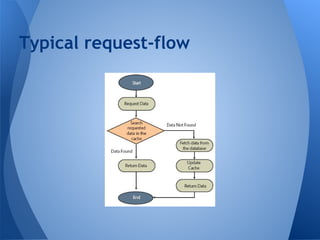
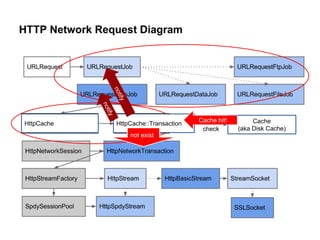
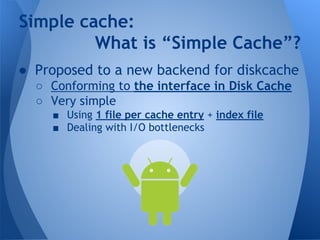
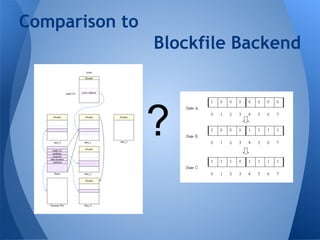
The document discusses Chromium's caching system. It describes the overall network stack and cache flow, including the disk cache which stores web resources on disk. It then focuses on the "simple cache" implementation, a new backend for disk cache that uses one file per cache entry and an index file for faster lookups. The simple cache aims to be more resilient to corruption, reduce delays, and have lower memory and disk usage than the existing blockfile backend.


















![References
[1] Disk Cache
[2] Disk Cache 3.0
[3] Very Simple Cache
[4] Multi-process Resource Loading
[5] Network Stack
[6] Network Stack Use in Chromium](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cacheinchromium-diskcache-140912113647-phpapp01/85/Cache-in-Chromium-Disk-Cache-28-320.jpg)