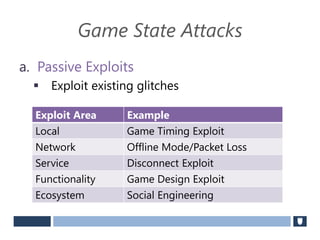
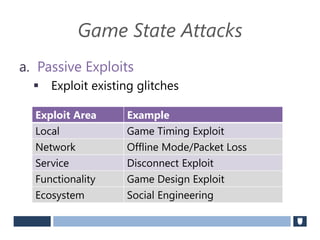
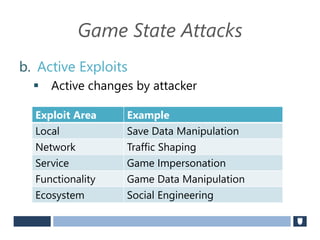
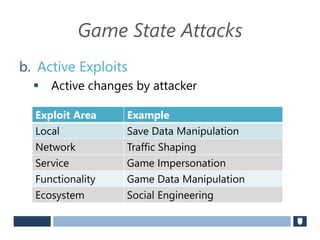
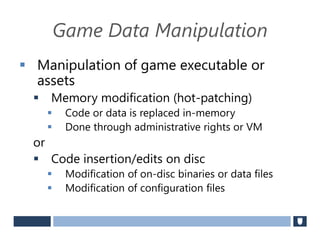
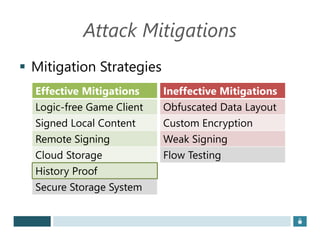
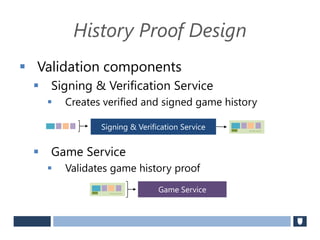
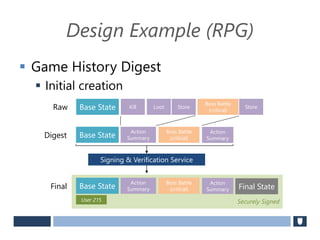
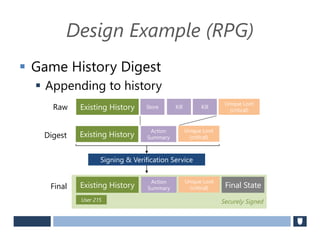
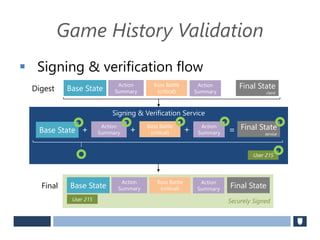
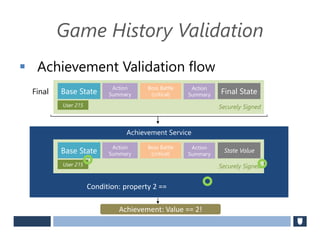
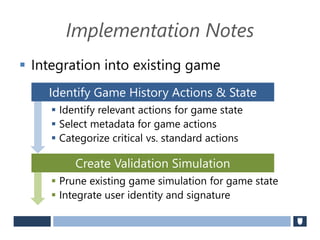
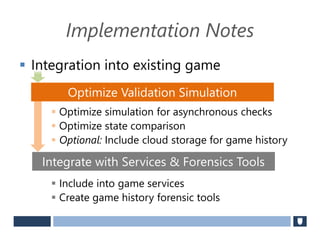
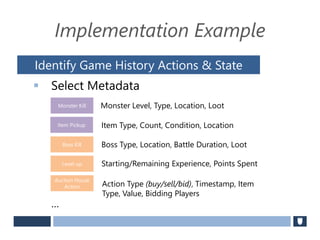
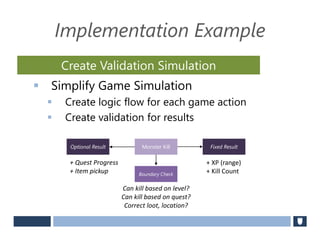
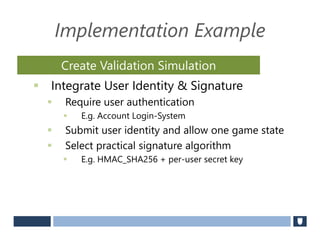
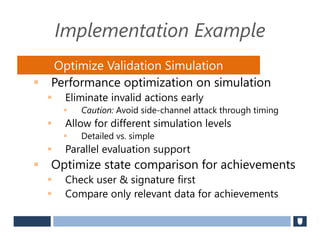
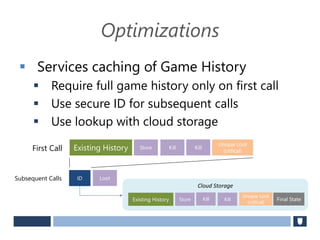
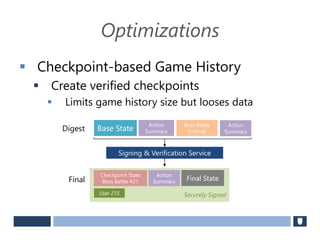
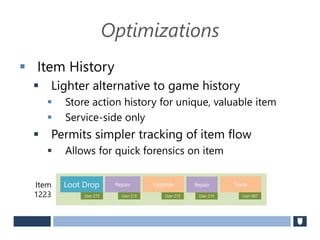
The document discusses using game history proofs to secure game achievements and prevent cheating. A history proof system would record all relevant game actions and states with a digital signature. A validation service would verify the game history is consistent when checking for achievements. This prevents cheaters from altering their local save data or manipulating game states.