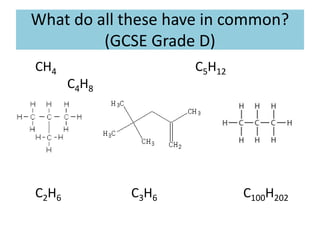
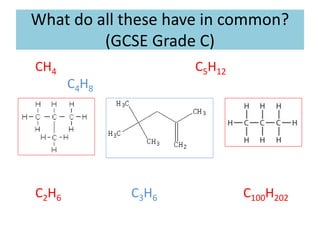
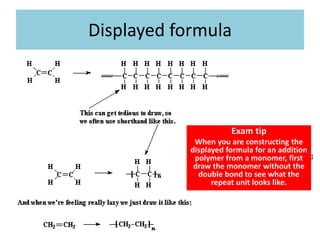
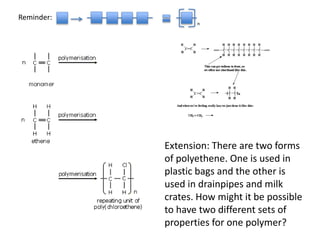
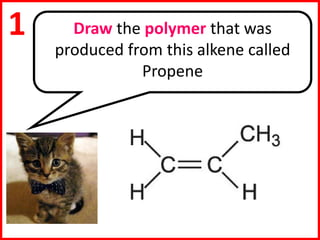
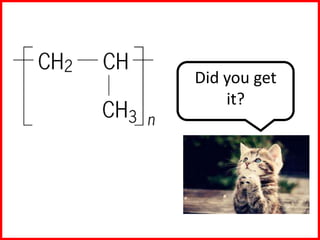
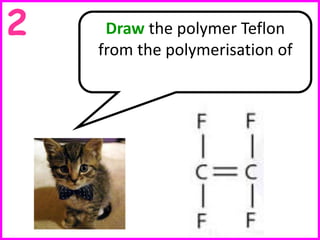
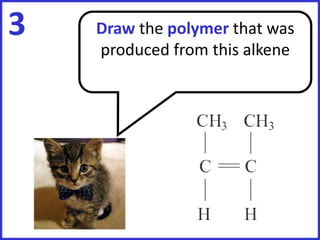
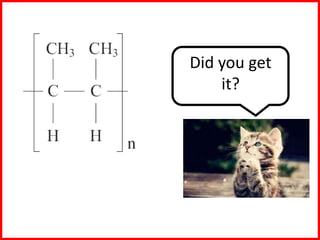
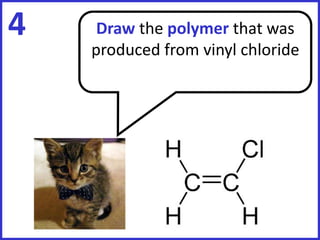
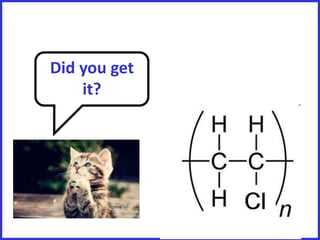
This document discusses a lesson on polymerization. It includes objectives about hydrocarbons, saturated and unsaturated compounds, and addition polymerization. Students are asked questions to test their understanding, including defining hydrocarbons, the difference between saturated and unsaturated compounds, explaining the bromine test for alkenes, drawing formulas for ethene and its polymer, and modeling polymerization. The document provides feedback on student responses and discussion of polymer properties.