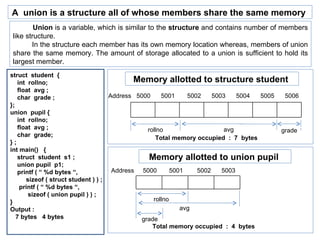
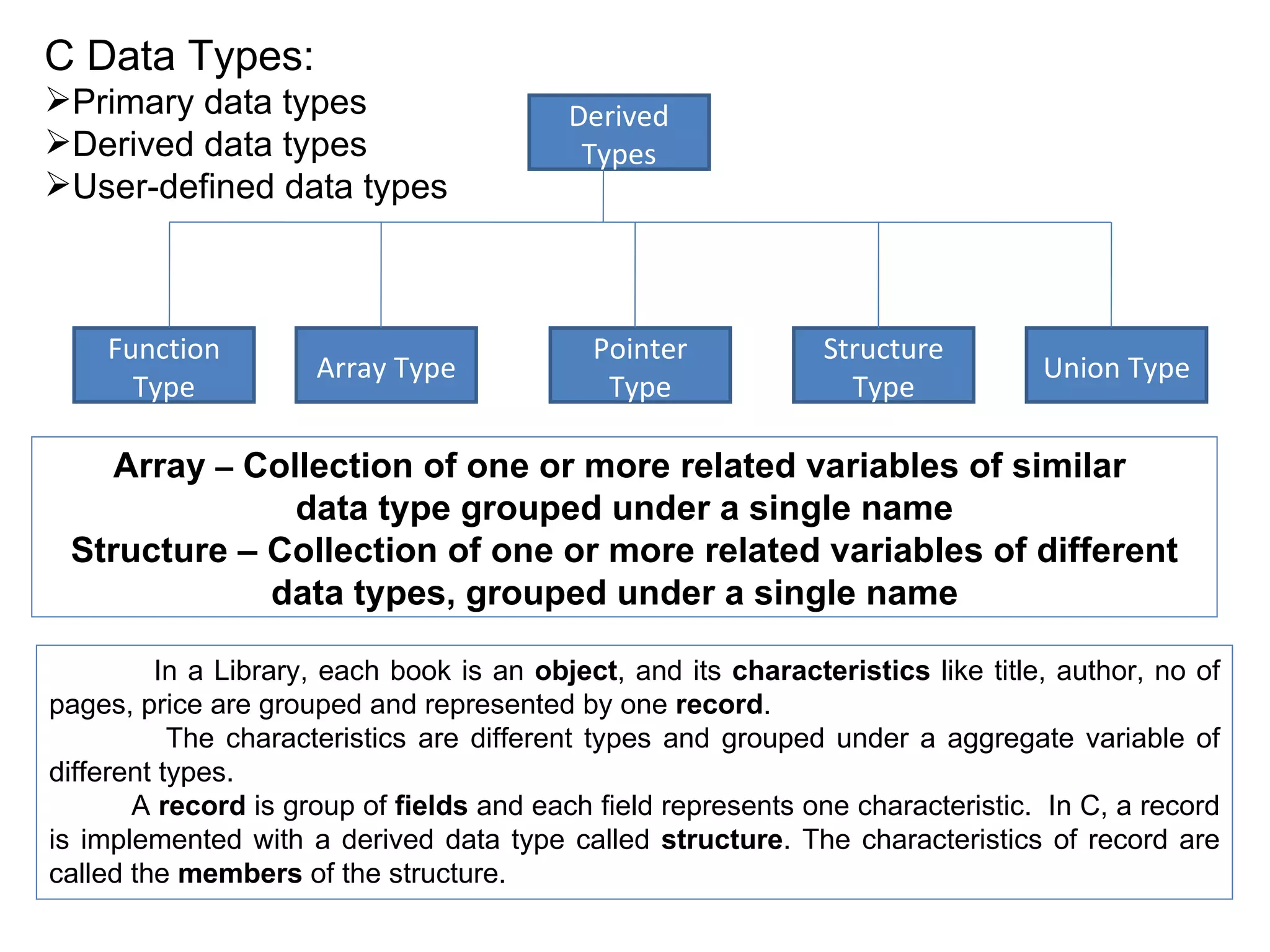
The document discusses C data types including primary, derived, and user-defined data types. It provides details on array and structure data types. Structures allow grouping of related data of different types under a single name. Structures can contain nested structures and pointers to structures. Pointers to structures allow accessing structure members using dot and arrow operators. Arrays of structures and self-referential structures are also discussed.
![Book-1 Book-2 Book-3
BookID: 1211 BookID: 1212 BookID: 1213
Title : C Primer Plus Title : The ANSI C Programming Title : C By Example
Author : Stephen Prata Author : Dennis Ritchie Author : Greg Perry
Pages : 984 Pages : 214 Pages : 498
Price : Rs. 585.00 Price : Rs. 125.00 Price : Rs. 305.00
book book_id integer 2 bytes
bookid
title Array of 50 characters 50 bytes
title
author Array of 40 characters 40 bytes
author
pages integer 2 bytes
pages
price price float 4 bytes
Memory occupied by a Structure variable
STRUCTURE- BOOK struct < structure_tag_name >
struct book { {
Structure tag data type < member 1 >
int book_id ;
char title[50] ; data type < member 2 >
…. …. …. ….
char author[40] ;
data type < member N >
int pages ; };
float price ;
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit4-120316085542-phpapp01/85/C-Language-Unit-4-2-320.jpg)
![Declaring a Structure Type Declaring a Structure Variable
struct student struct student s1,s2,s3;
{ (or)
int roll_no; struct student
char name[30]; {
float percentage; int roll_no;
}; char name[30];
float percentage;
}s1,s2,s3;
Initialization of structure Reading values to members at
runtime:
Initialization of structure variable while
declaration : struct student s3;
struct student s2 = { 1001, “ K.Avinash ”, printf(“nEnter the roll no”);
87.25 } ; scanf(“%d”,&s3.roll_no);
Initialization of structure members individually : printf(“nEnter the name”);
s1. roll_no = 1111; scanf(“%s”,s3.name);
strcpy ( s1. name , “ B. Kishore “ ) ; printf(“nEnter the percentage”);
s1.percentage = 78.5 ; scanf(“%f”,&s3.percentage);
membership operator](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit4-120316085542-phpapp01/85/C-Language-Unit-4-3-320.jpg)
![Implementing a Structure
struct employee {
int empid;
char name[35];
int age; Declaration of Structure Type
float salary;
};
Declaration of Structure variables
int main() {
struct employee emp1,emp2 ; Declaration and initialization of Structure variable
struct employee emp3 = { 1213 , ” S.Murali ” , 31 , 32000.00 } ;
emp1.empid=1211;
strcpy(emp1.name, “K.Ravi”);
emp1.age = 27; Initialization of Structure members individually
emp1.salary=30000.00;
printf(“Enter the details of employee 2”); Reading values to members of Structure
scanf(“%d %s %d %f “ , &emp2.empid, emp2.name, &emp2.age, &emp2.salary);
if(emp1.age > emp2.age)
printf( “ Employee1 is senior than Employee2n” );
else
printf(“Employee1 is junior than Employee2n”);
Accessing members of Structure
printf(“Emp ID:%dn Name:%sn Age:%dn Salary:%f”,
emp1.empid,emp1.name,emp1.age,emp1.salary);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit4-120316085542-phpapp01/85/C-Language-Unit-4-4-320.jpg)
![Arrays And structures Nesting of structures
struct student struct date {
{ int day ;
int sub[3] ; int month ;
Outer Structure
int total ; int year ;
}; };
struct person {
char name[40];
int main( ) { int age ;
struct student s[3]; struct date b_day ;
int i,j; };
for(i=0;i<3;i++) { int main( ) { Inner Structure
printf(“nnEnter student %d marks:”,i+1); struct person p1;
for(j=0;j<3;j++) { strcpy ( p1.name , “S. Ramesh “ ) ;
scanf(“%d”,&s[i].sub[j]); p1. age = 32 ;
} p1.b_day.day = 25 ; Accessing Inner
} p1.b_day. month = 8 ; Structure members
for(i=0;i<3;i++) { p1.b_day. year = 1978 ;
s[i].total =0; }
for(j=0;j<3;j++) {
s[i].total +=s[i].sub[j]; OUTPUT:
} Enter student 1 marks: 60 60 60
printf(“nTotal marks of student %d is: %d”, Enter student 2 marks: 70 70 70
i+1,s[i].total ); Enter student 3 marks: 90 90 90
}
} Total marks of student 1 is: 180
Total marks of student 2 is: 240
Total marks of student 3 is: 270](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit4-120316085542-phpapp01/85/C-Language-Unit-4-5-320.jpg)
![structures and functions Self referential structures
struct fraction { struct student_node {
int numerator ; int roll_no ;
int denominator ; char name [25] ;
}; struct student_node *next ;
};
void show ( struct fraction f ) int main( )
{ {
printf ( “ %d / %d “, f.numerator, struct student_node s1 ;
struct student_node s2 = { 1111, “B.Mahesh”, NULL } ;
f.denominator ) ; s1. roll_no = 1234 ;
} strcpy ( s1.name , “P.Kiran “ ) ;
int main ( ) { s1. next = & s2 ; s2 node is linked to s1 node
struct fraction f1 = { 7, 12 } ;
show ( f1 ) ; printf ( “ %s “, s1. name ) ;
} Prints P.Kiran
printf ( “ %s “ , s1.next - > name ) ; Prints B.Mahesh
OUTPUT: }
7 / 12
A self referential structure is one that includes at least one member
which is a pointer to the same structure type.
With self referential structures, we can create very useful data
structures such as linked -lists, trees and graphs.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit4-120316085542-phpapp01/85/C-Language-Unit-4-6-320.jpg)
![Pointer to a structure
struct product Accessing structure members through
{ pointer :
int prodid;
char name[20]; i) Using . ( dot ) operator :
}; ( *ptr ) . prodid = 111 ;
strcpy ( ( *ptr ) . Name, “Pen”) ;
int main()
{ ii) Using - > ( arrow ) operator :
struct product inventory[3]; ptr - > prodid = 111 ;
struct product *ptr; strcpy( ptr - > name , “Pencil”) ;
printf(“Read Product Details : n");
for(ptr = inventory;ptr<inventory +3;ptr++) {
scanf("%d %s", &ptr->prodid, ptr->name); Read Product Details :
}
111 Pen
printf("noutputn");
112 Pencil
for(ptr=inventory;ptr<inventory+3;ptr++) 113 Book
{
printf("nnProduct ID :%5d",ptr->prodid); Print Product Details :
printf("nName : %s",ptr->name);
} Product ID : 111
} Name : Pen
Product ID : 112
Name : Pencil
Product ID : 113
Name : Book](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit4-120316085542-phpapp01/85/C-Language-Unit-4-7-320.jpg)