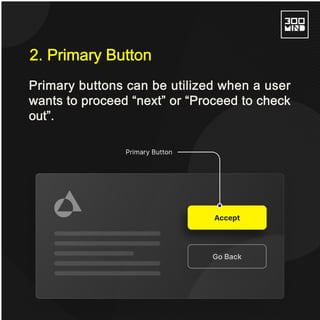
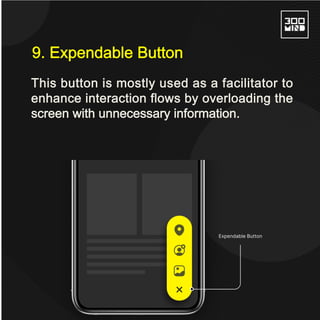
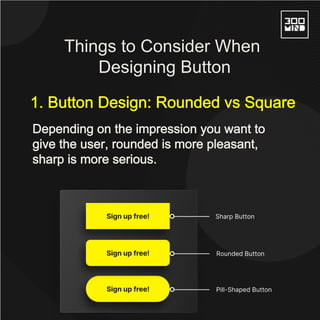
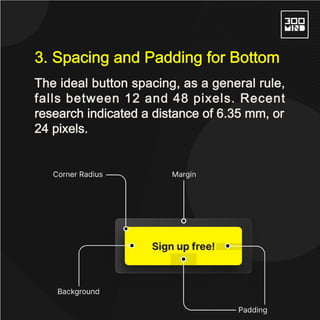
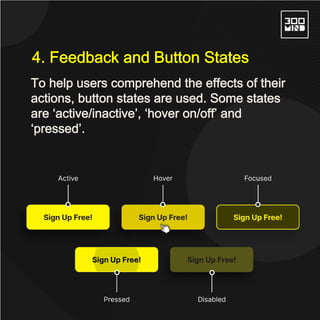
The document discusses the various types of buttons in design, including primary, secondary, ghost, toggle, and floating action buttons, each serving different user interaction purposes. It also covers button design considerations such as shape, spacing, feedback, and the impact of color on user behavior. Additionally, the importance of microcopy in conveying actions associated with buttons is emphasized.