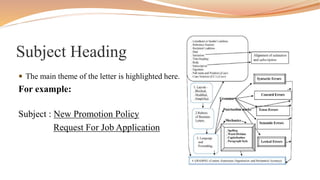
The document discusses the definition, purpose, structure, and types of business letters. It provides tips for writing effective business letters and explains the typical parts of a business letter including the letterhead, salutation, body, complimentary close, and signature. Examples are given of different types of business letters like sales letters, order letters, and complaint letters.