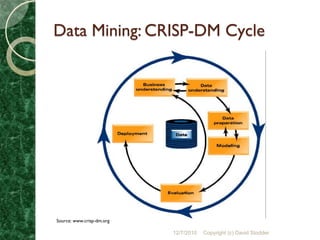
This webcast discussed advanced analytics in practice. It began with setting the context for analytics by defining key terms like analytics, business intelligence (BI), and discussing trends like democratizing analytics. It then covered how information management infrastructure is critical for analytics. Advanced analytics strategies were discussed, including predictive analytics, data mining, and examples of their use. Best practices emphasized using templates and pre-configured systems to make analytics more affordable and focusing modeling on business outcomes. The webcast concluded with a question and answer session.