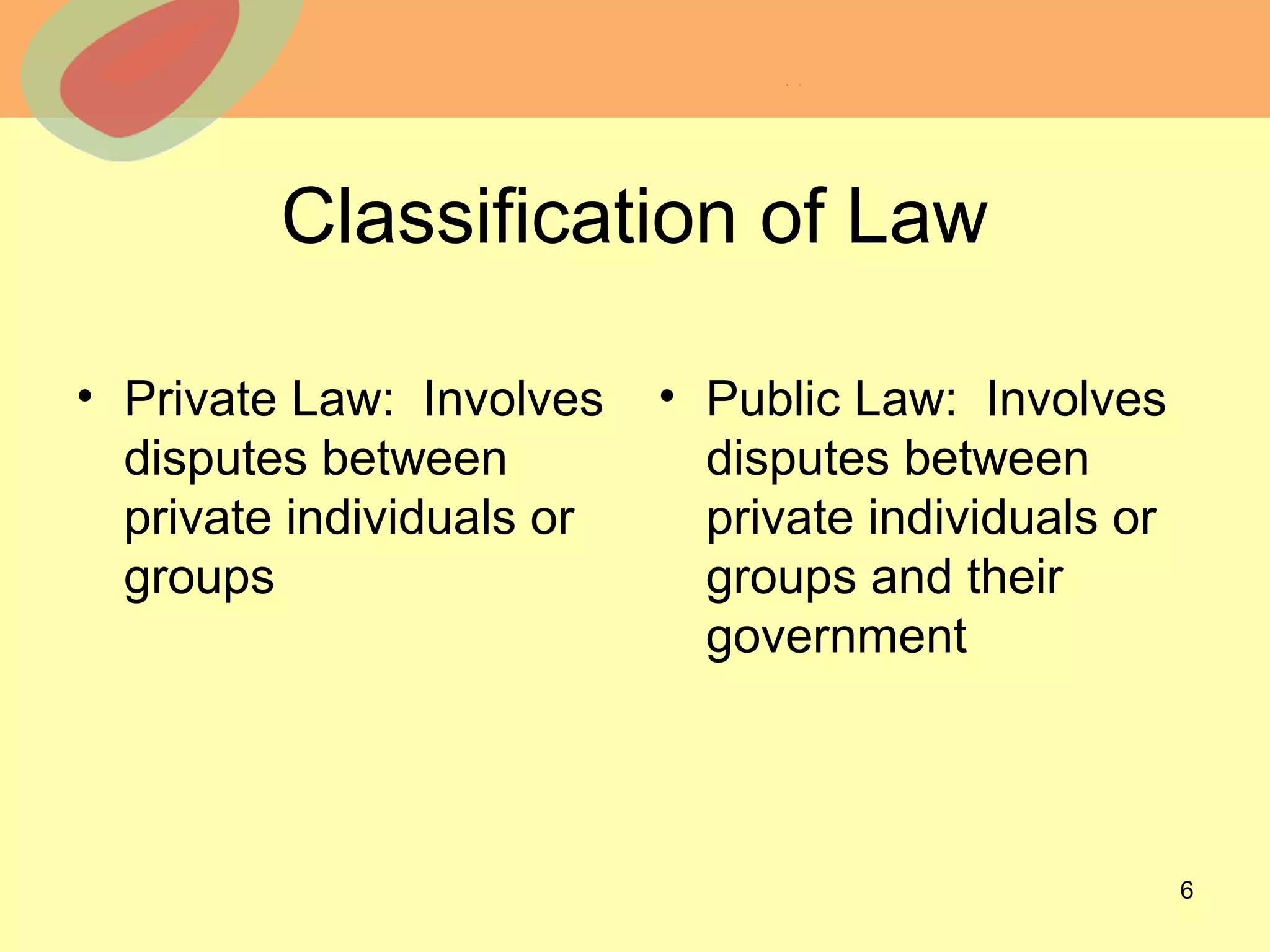
A group of legal professionals have proposed a uniform criminal code that would create consistency across states by standardizing definitions of misdemeanors and felonies, how crimes are defined, and punishments. The proposed code would abolish the death penalty and cap punishment for murder at life in prison. The document discusses potential advantages of increased uniformity but also questions whether states would agree to replace their own criminal laws.