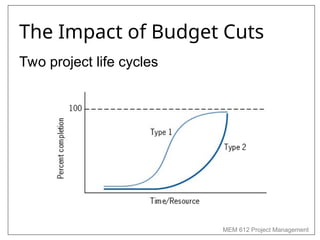
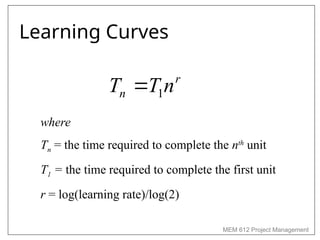
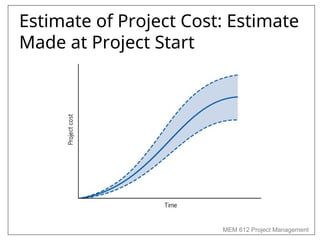
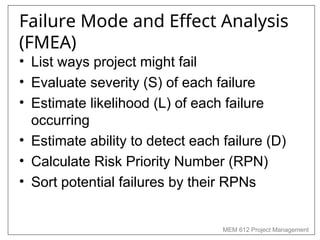
Chapter 4 of MEM 612 discusses project budgeting as a method for allocating resources and costs to project activities, linking them to organizational objectives. It outlines two budgeting methods: top-down, which relies on managerial estimates, and bottom-up, which is based on detailed task estimations. The chapter also covers cost estimating, budget uncertainty, risk management, and other factors affecting project budgeting.