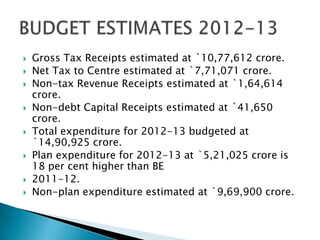
The document summarizes key points from the Indian Union Budget for 2012-13. It discusses estimates for GDP growth, fiscal deficits, revenues and expenditures. It outlines proposals to increase investment in infrastructure, manufacturing, rural development and social sectors. Taxation measures are also highlighted, including increases in excise duties and service tax rates, while personal income tax exemptions are raised. The budget aims to boost growth while reducing fiscal deficits.