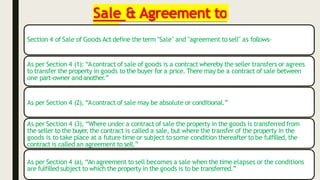
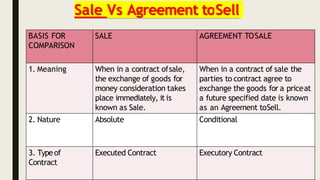
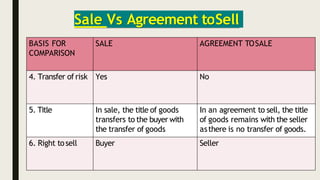
This document provides an overview of the Sale of Goods Act 1930 in India. It defines key terms like "sale" and "agreement to sell" and outlines the essential elements of a contract of sale. A sale involves the immediate transfer of ownership of goods from the seller to the buyer in exchange for payment. An agreement to sell establishes that this transfer will occur at a future date or once certain conditions are met. The document compares and contrasts sales with agreements to sell on factors like the nature of the contract, transfer of risk/title, tax implications, and remedies available in a breach. It concludes with thanking the reader for their time.