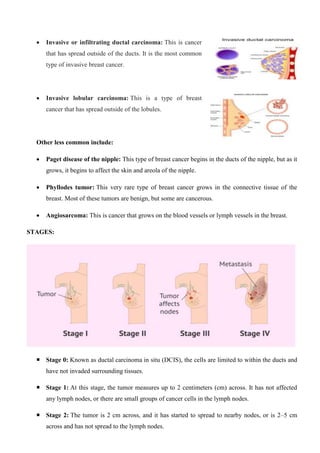
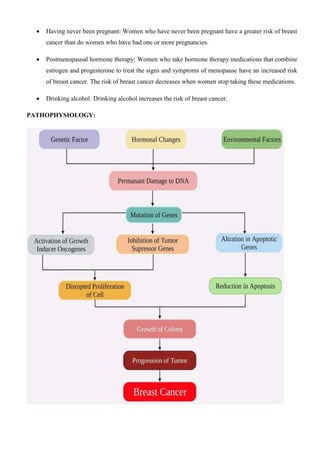
Breast cancer is the most common invasive cancer in women and the second leading cause of cancer death. It begins in the cells of the breast, usually the ducts or lobules, and can be invasive or non-invasive. Risk factors include being female, increasing age, family history, genetic factors, lifestyle factors like obesity, alcohol use, and reproductive factors. Symptoms may include a breast lump or changes to the breast or nipple. Treatment involves surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, hormone therapy, and targeted therapy depending on the cancer type and stage. Prevention strategies incorporate maintaining a healthy weight, being physically active, limiting alcohol, and breastfeeding.