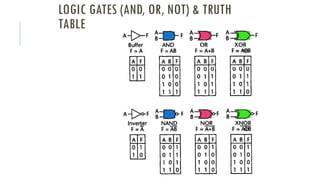
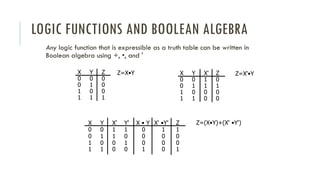
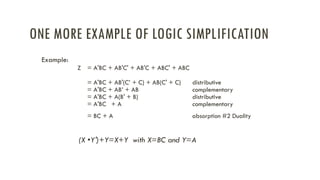
Lecture 3 covers boolean algebra and logic gates, explaining its foundational role in computation by operating with binary values of 0's and 1's. It introduces axioms, laws, and theorems that facilitate the design and simplification of logic functions and expresses them through truth tables and logic gates. Key concepts include duality and De Morgan's theorem, which aid in complementing boolean functions and simplifying expressions.