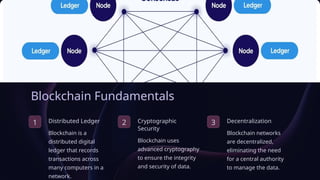
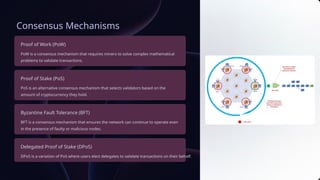
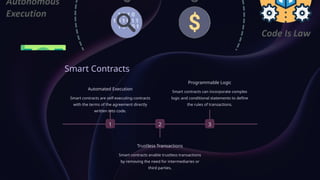
The document provides an overview of blockchain technology, including its fundamentals, distributed ledger characteristics, cryptographic security, consensus mechanisms, and applications across various industries such as finance, supply chain, and healthcare. It addresses the challenges of scalability, regulatory uncertainty, and energy consumption, while also highlighting emerging trends such as interoperability and decentralized finance. Ultimately, the document underscores blockchain's transformative potential but emphasizes the need to overcome existing limitations.