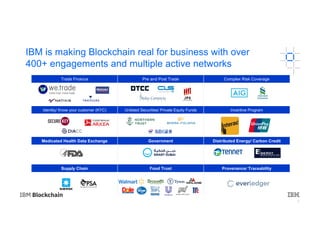
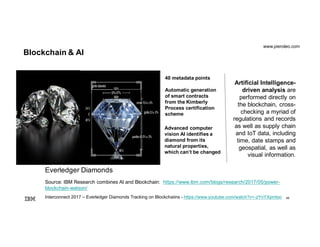
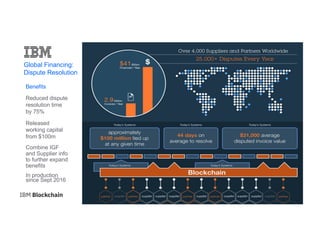
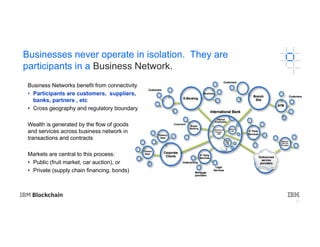
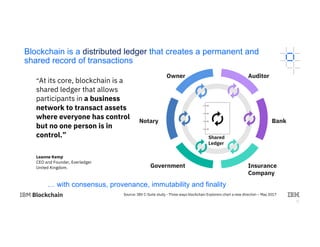
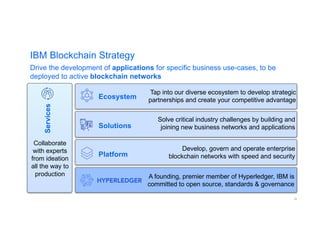
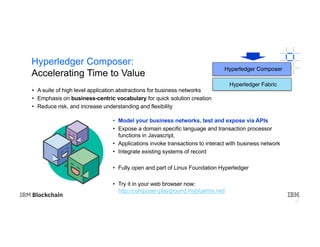
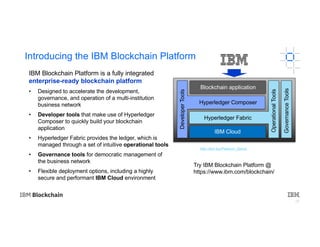
The document provides an introduction to blockchain technology's applications in business, emphasizing its potential to enhance ecosystems, streamline processes, and reduce risks through transparency and a decentralized ledger. IBM highlights its engagement in multiple sectors using blockchain, including trade finance, supply chain, and healthcare, projecting significant economic benefits. Furthermore, it discusses the IBM blockchain platform and Hyperledger project, designed to develop and govern enterprise blockchain networks for improved collaboration and operational efficiency.