Embed presentation
Download to read offline

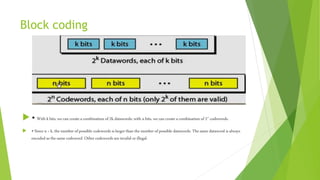

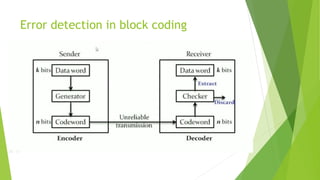

Block coding takes message data and divides it into blocks of k bits called data words. It then adds r redundant bits to each block, making the block length n=k+r bits, called a code word. There are 2^k possible data words but 2^n possible code words since n is larger than k, allowing some code words to be invalid or illegal and ensure the same data word is always encoded as the same code word.





