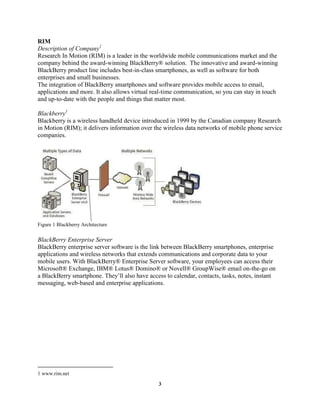
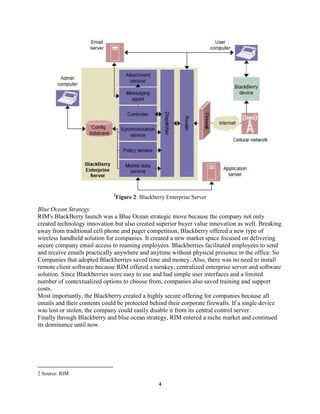
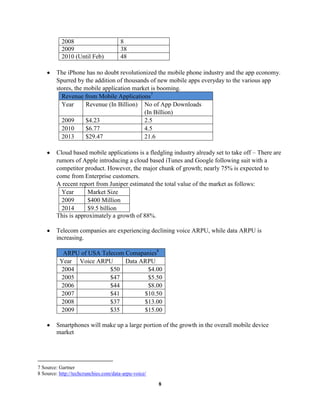
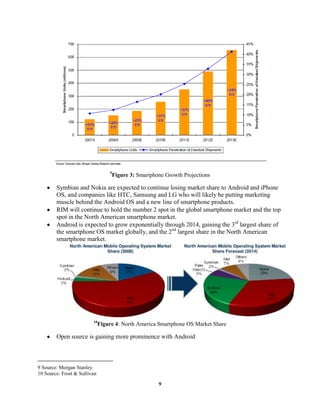
The document provides an overview and analysis of Research In Motion (RIM) and their Blackberry smartphones. It describes RIM's history and products, including the Blackberry and Blackberry Enterprise Server. It then performs a SWOT analysis and discusses RIM's original "Blue Ocean Strategy". The focus is stated as using scenario analysis to identify potential threats to Blackberry's dominant position and strategies for RIM to address those threats over the next 3-5 years. An analysis of the smartphone industry and Porter's 5 Forces model is also presented.