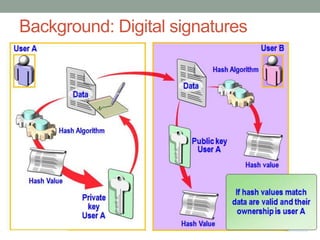
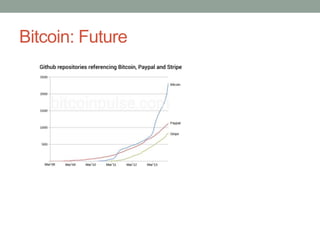
Bitcoin uses a decentralized, distributed peer-to-peer network to maintain a public ledger of transactions without the need for a central authority. Miners on the network verify transactions and group them into blocks, competing to be the first to solve complex cryptographic puzzles. Whichever miner solves the puzzle first broadcasts the verified block of transactions to the network, receiving a reward of newly created bitcoins. This process of proof-of-work prevents fraud by making the blockchain history difficult to modify. The network difficulty adjusts to keep block generation at around 10 minutes, and the longest blockchain is accepted as the valid history by consensus.