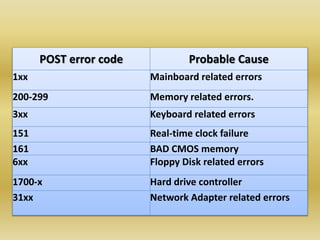
BIOS initializes hardware at startup and allows access to CMOS settings. CMOS stores settings like time, date, and boot order and is powered by a battery. The POST tests hardware at startup and may display error codes for failed components. BIOS can be upgraded via flashing and CMOS restored via jumper to factory defaults.