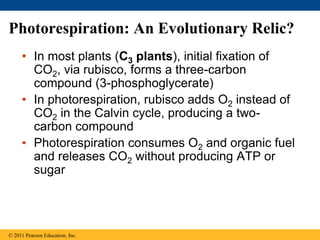
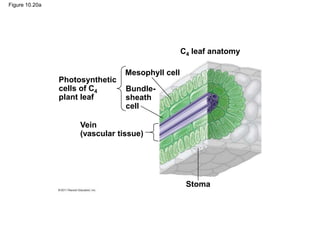
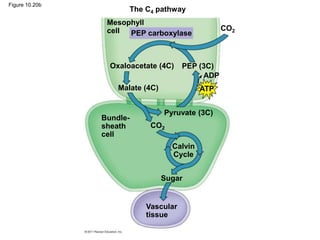
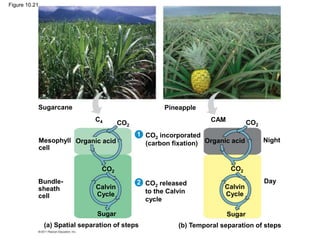
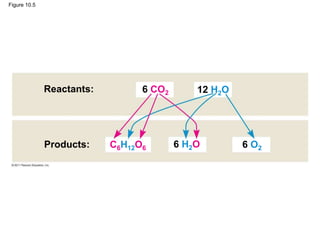
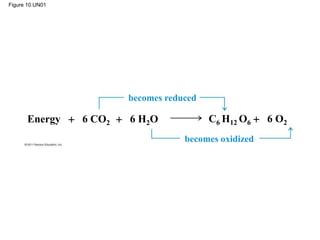
1. Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria use sunlight, water and carbon dioxide to produce oxygen and energy in the form of ATP and NADPH.
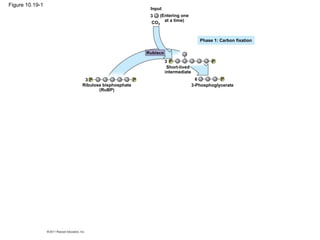
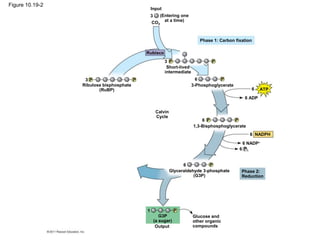
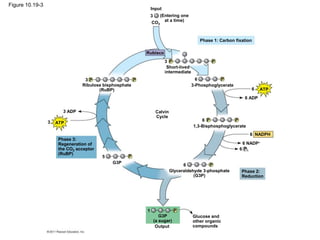
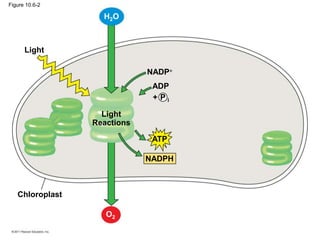
2. It occurs in two stages - the light-dependent reactions where solar energy is captured to make ATP and NADPH, and the light-independent Calvin cycle where carbon is incorporated into organic compounds using ATP and NADPH.
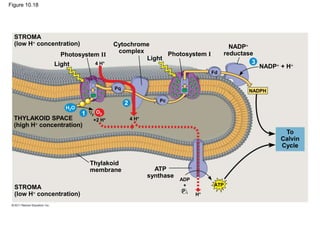
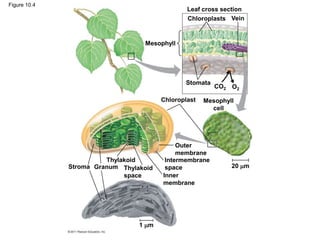
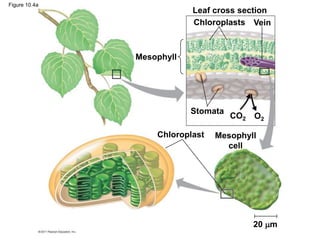
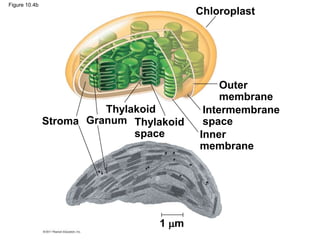
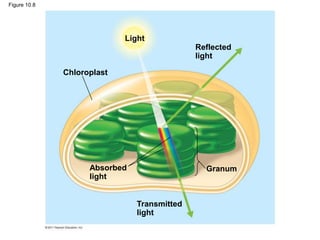
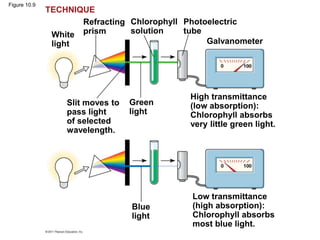
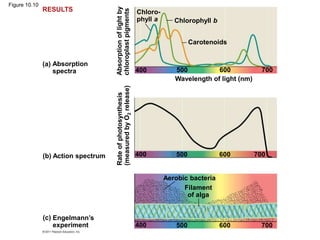
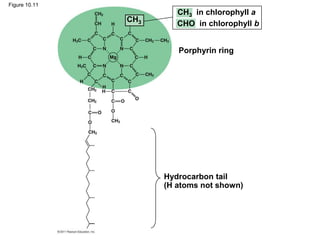
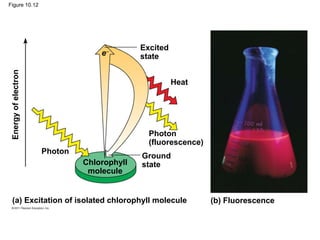
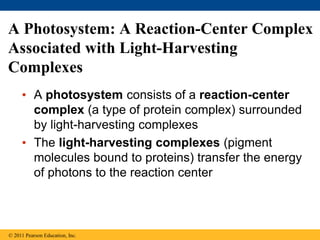
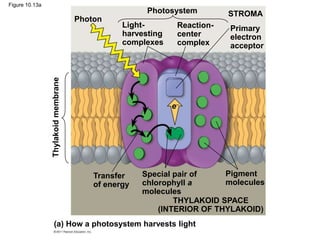
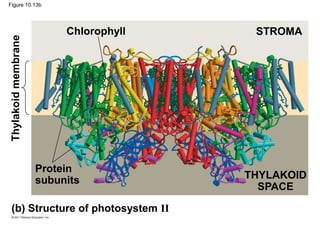
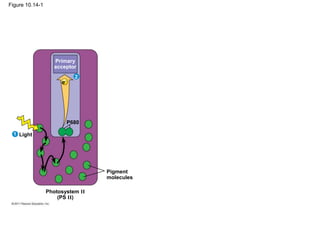
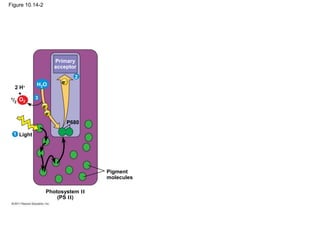
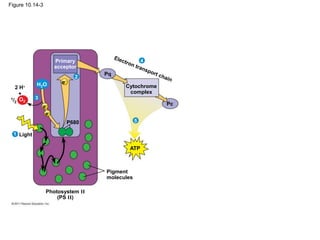
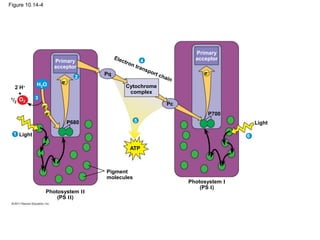
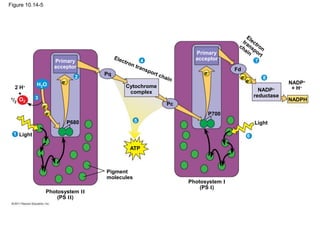
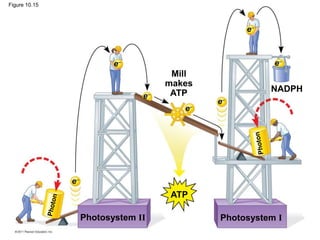
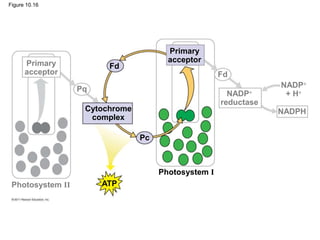
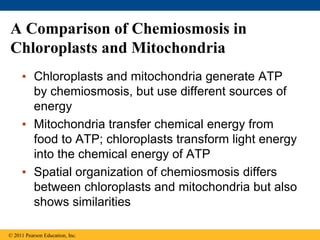
3. The light reactions take place in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts and utilize two photosystems, photosystem II and photosystem I, to transfer electrons down an electron transport chain and pump protons across the membrane, driving ATP synthesis.

















![Light
Light
Reactions
Calvin
Cycle
Chloroplast
[CH2O]
(sugar)
ATP
NADPH
NADP
ADP
+ P i
H2O CO2
O2
Figure 10.6-4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap10ppt-240317193419-862d3948/85/BioLogy-Photosynthesis-chapterr10ppt-ppt-25-320.jpg)



















![Mitochondrion Chloroplast
MITOCHONDRION
STRUCTURE
CHLOROPLAST
STRUCTURE
Intermembrane
space
Inner
membrane
Matrix
Thylakoid
space
Thylakoid
membrane
Stroma
Electron
transport
chain
H Diffusion
ATP
synthase
H
ADP P i
Key Higher [H ]
Lower [H ]
ATP
Figure 10.17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap10ppt-240317193419-862d3948/85/BioLogy-Photosynthesis-chapterr10ppt-ppt-64-320.jpg)