This document describes several biochemical tests used to identify bacteria based on their metabolism of carbohydrates and other substrates.
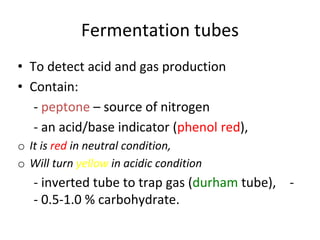
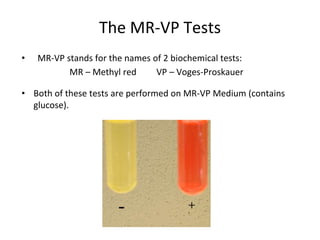
[1] Fermentation tests detect acid and gas production from carbohydrates like glucose, lactose, and sucrose. The MR-VP tests identify bacteria that produce acids or alcohols from glucose fermentation. The Methyl Red test checks for acid production and the Voges-Proskauer test detects alcohol production.
[2] The Citrate test examines bacteria's ability to use citrate as an energy source, indicated by a color change from green to blue. These tests are performed on bacterial isolates using fermentation tubes, MR-VP medium, and Simmons citrate agar