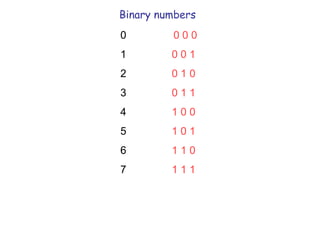
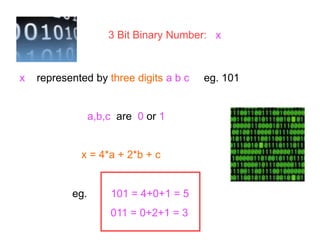
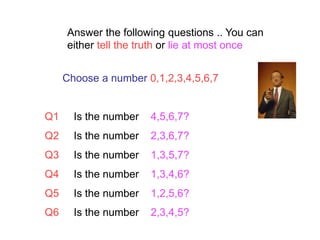
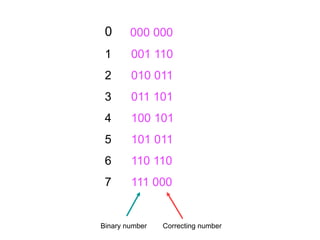
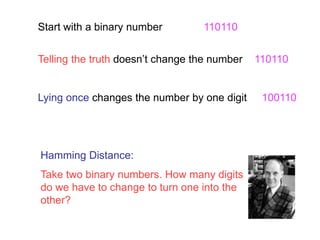
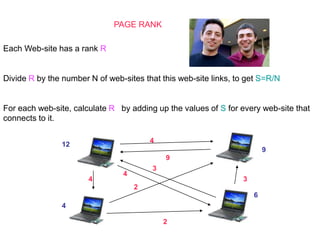
The document explores the fundamental role of mathematics in shaping the modern world, emphasizing its applications in technology, medicine, and information security. It highlights key mathematical concepts, such as binary numbers, error correction codes, and network theory, which underlie innovations like the internet and devices like the iPod. The text illustrates how mathematicians and their work are crucial for managing information and preventing errors in communication and data storage.