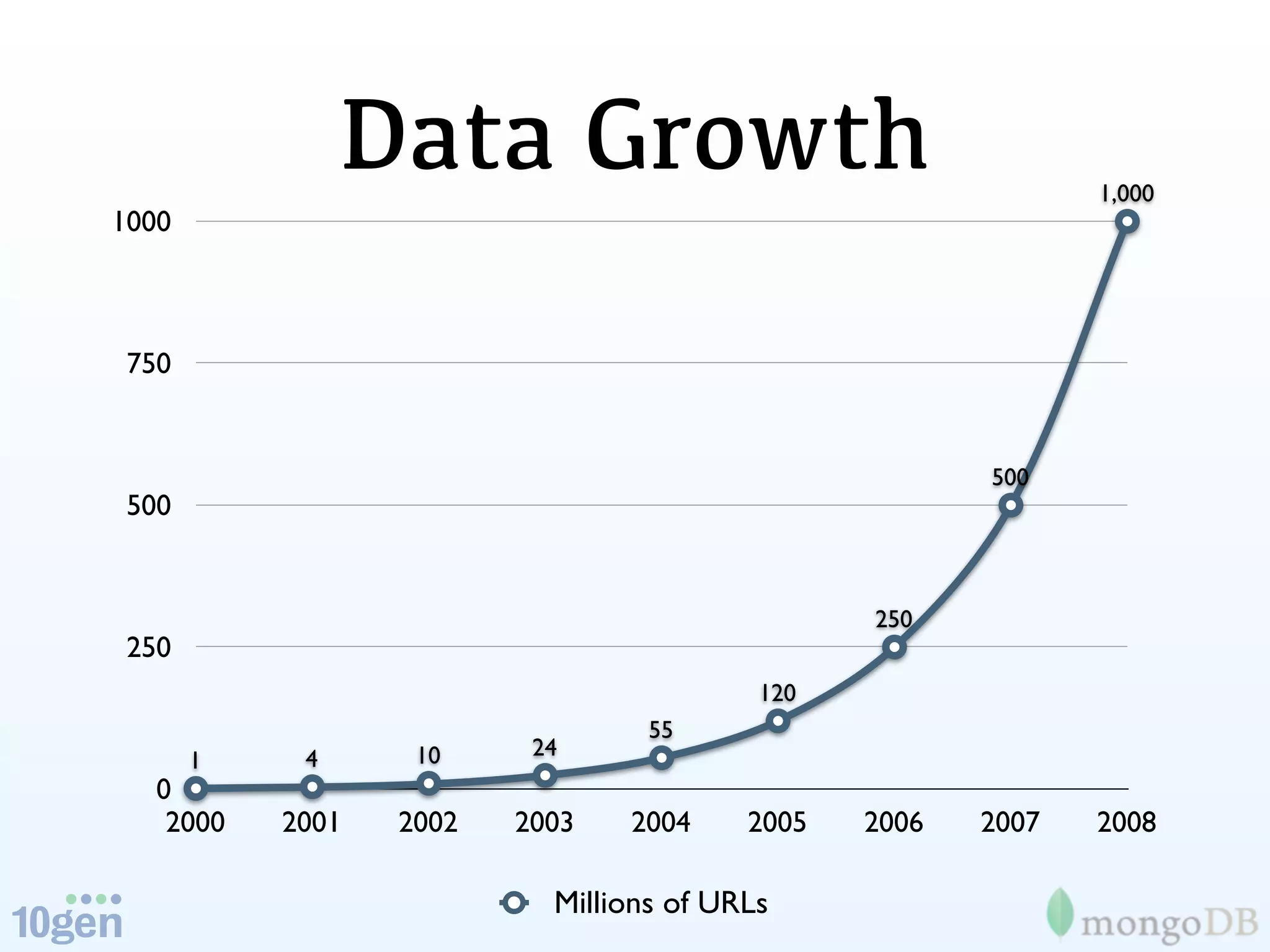
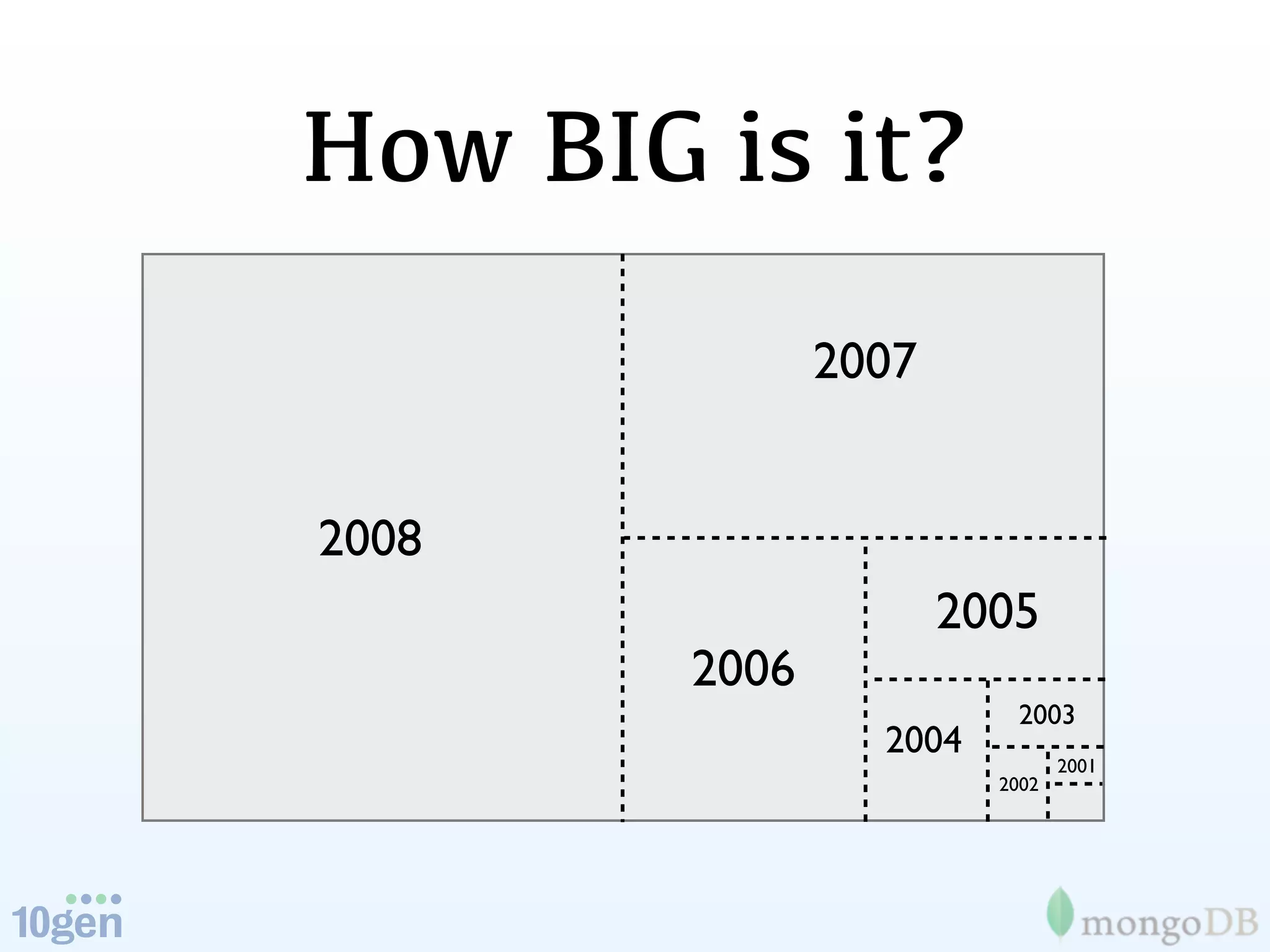
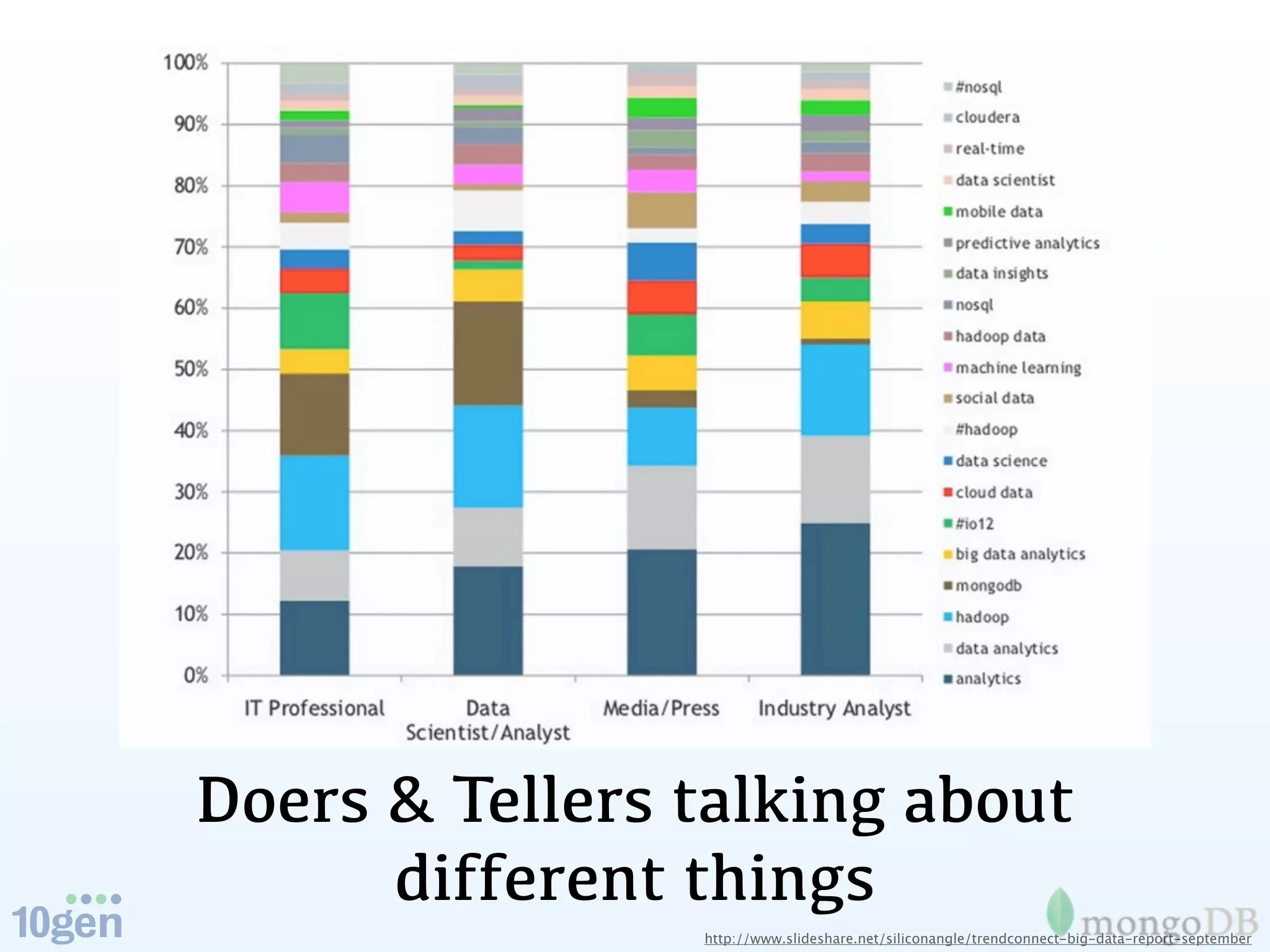
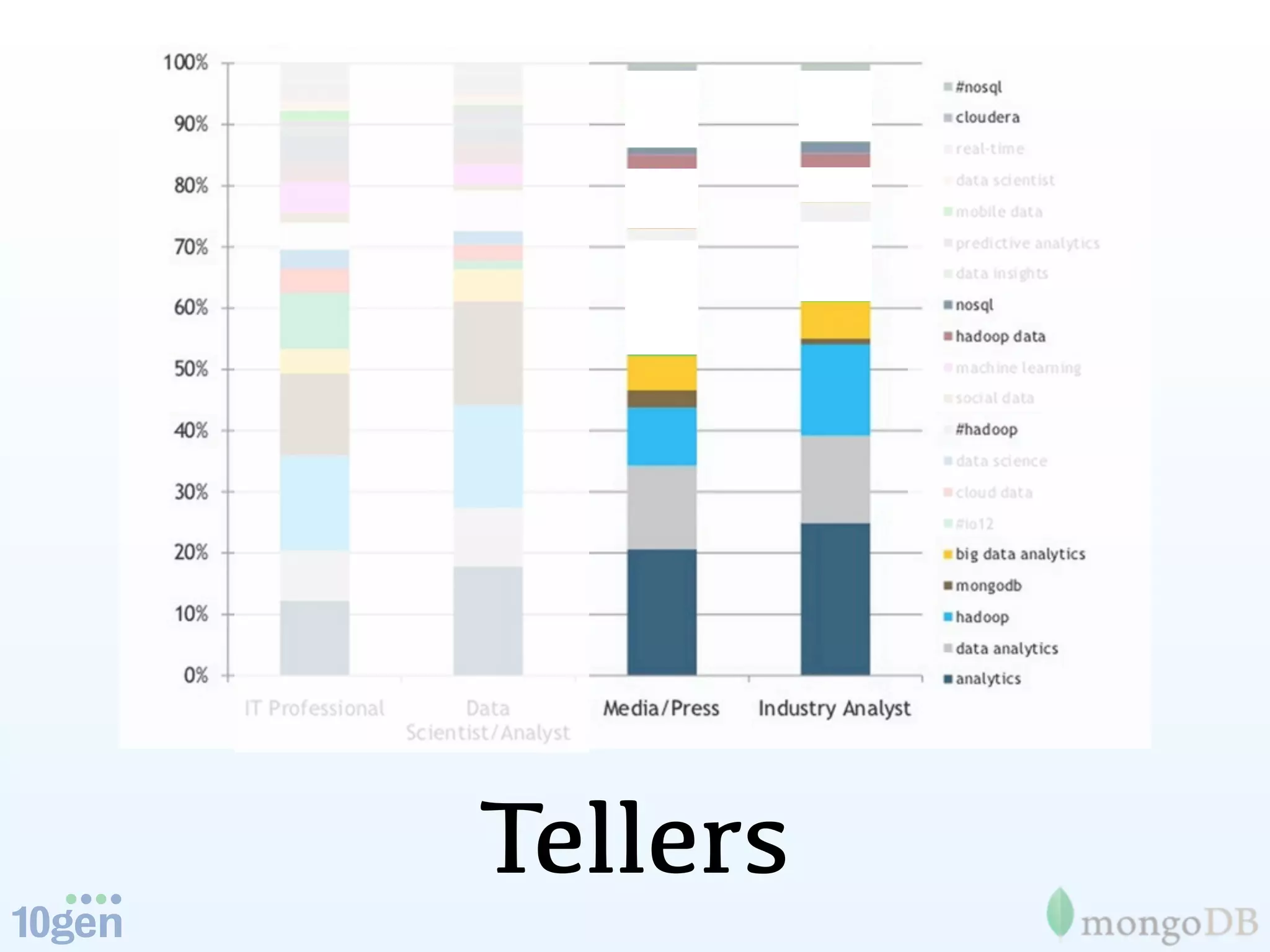
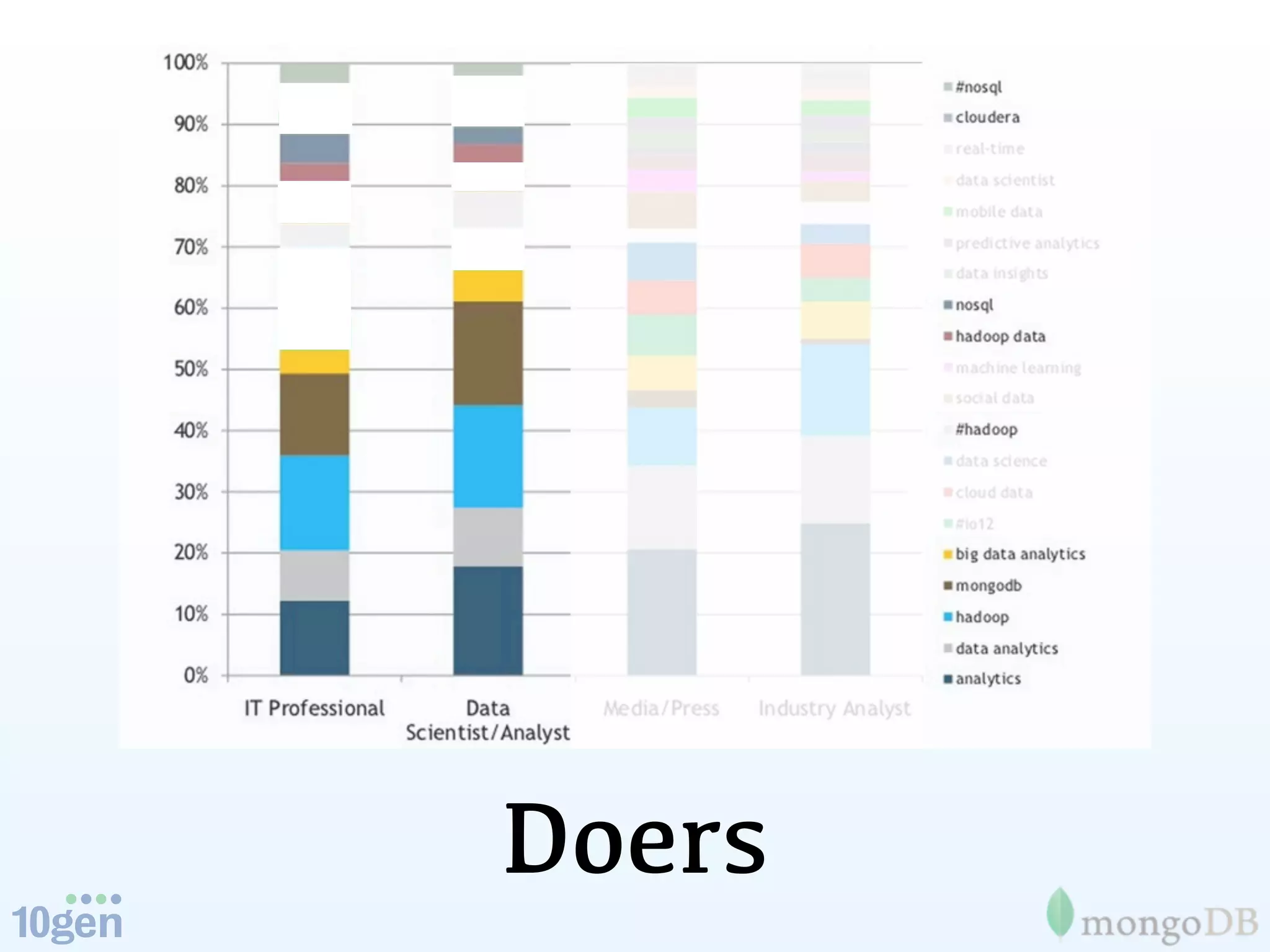
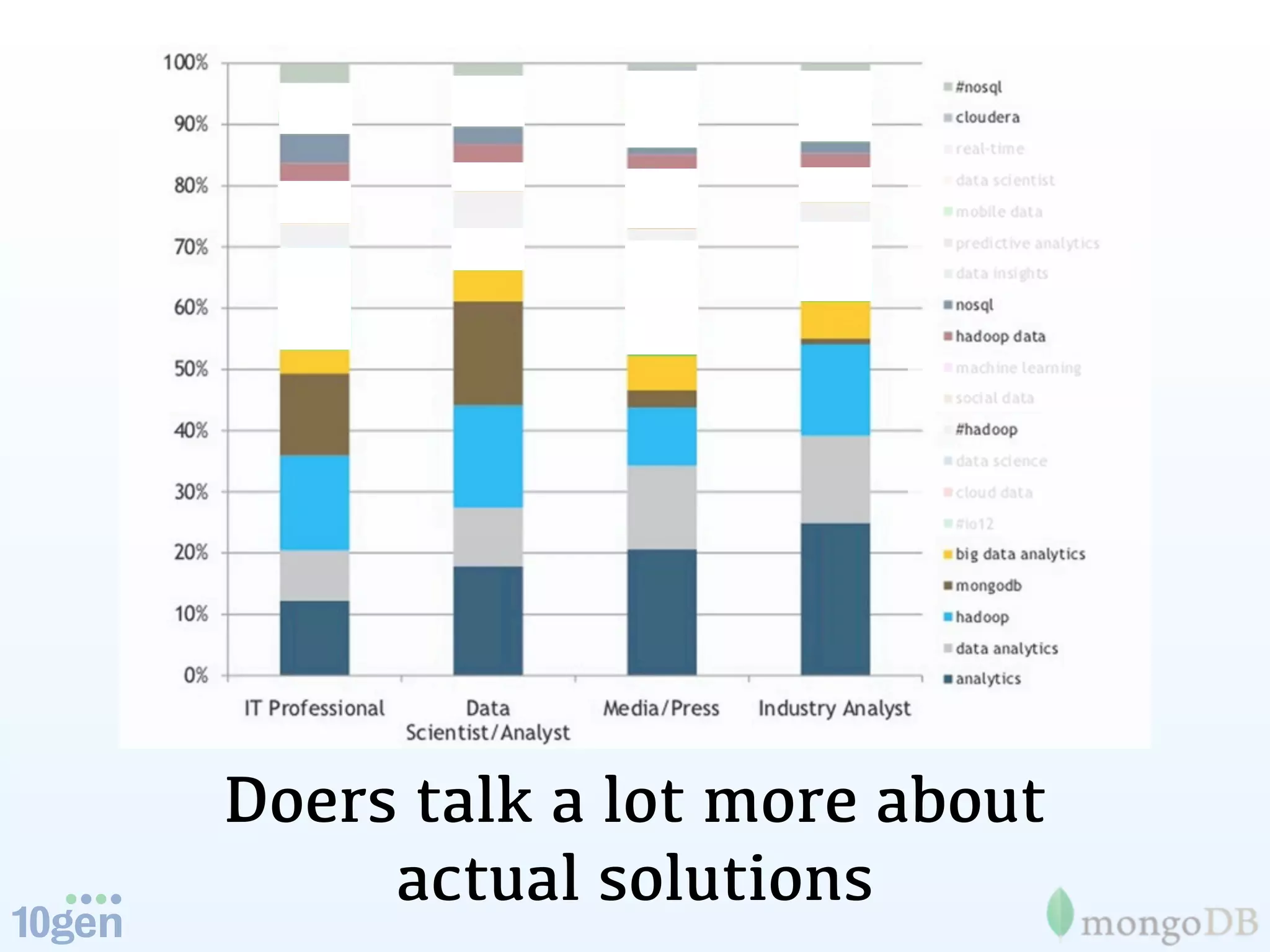
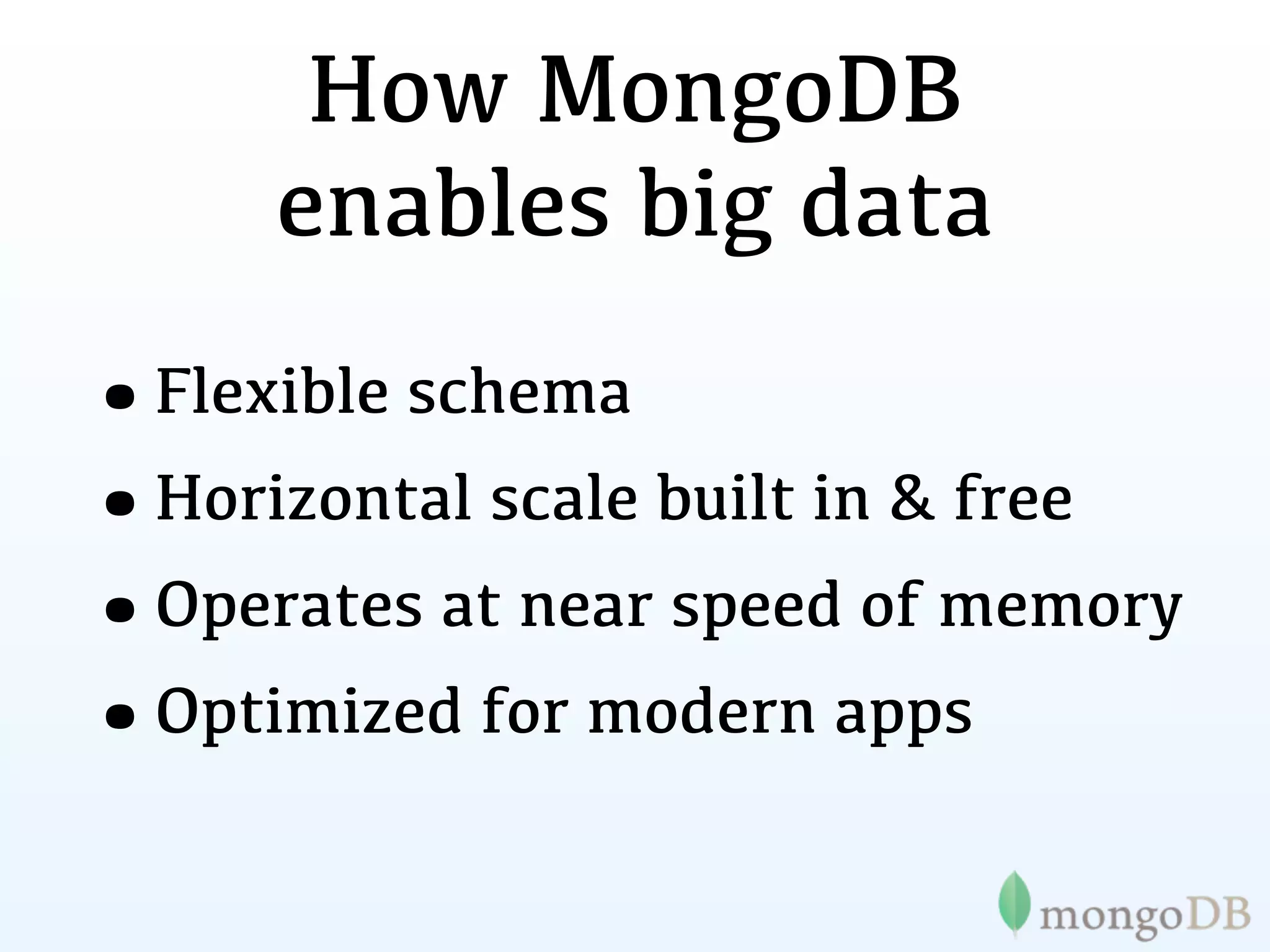
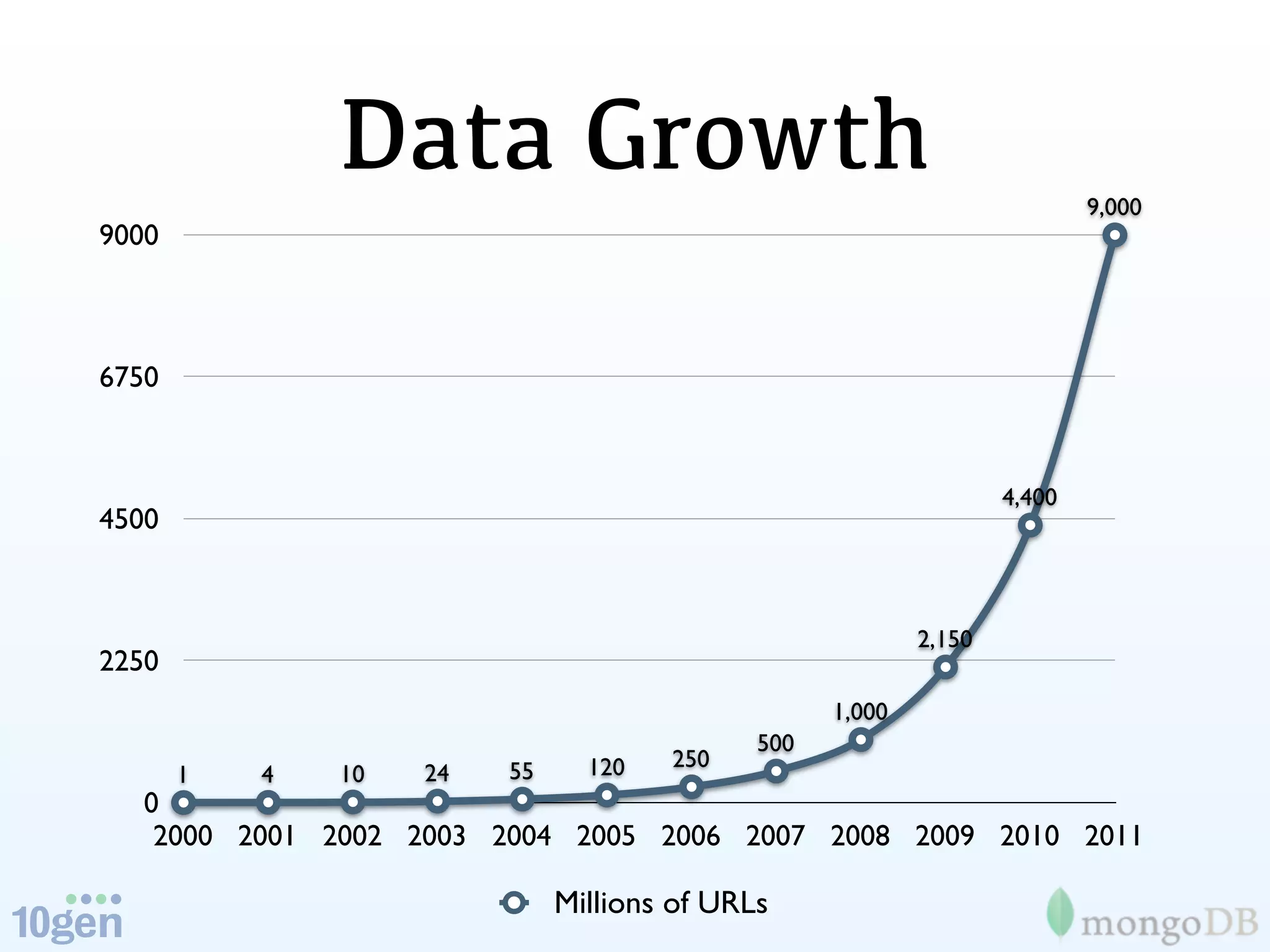
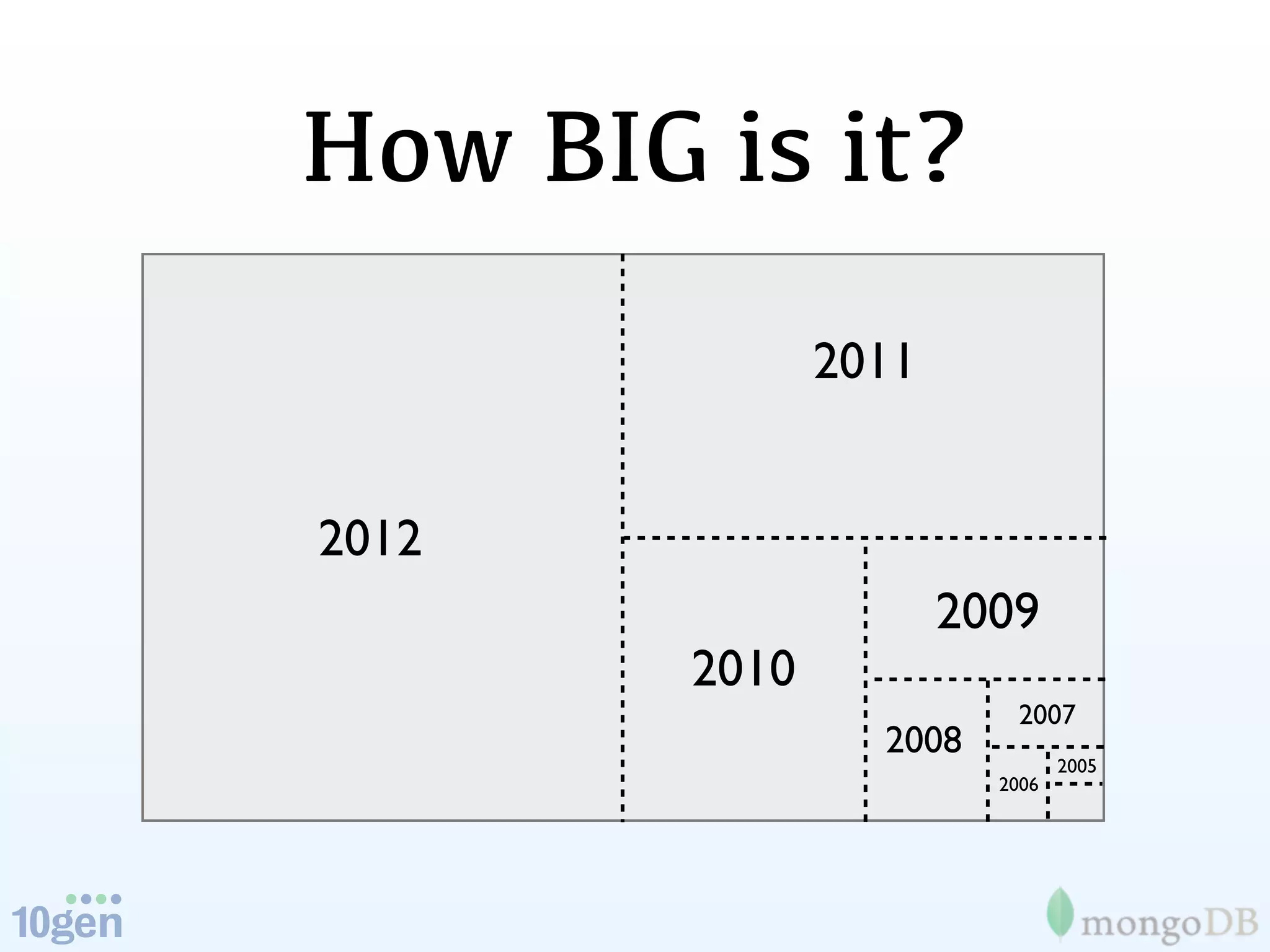
The document discusses the evolution and significance of big data, highlighting its exponential growth and the need for custom software in handling it. It emphasizes the roles of technologies like MongoDB and Hadoop in storage and processing, exemplified through real-world applications such as Orbitz's hotel data collection. The future of big data is portrayed as a constantly evolving landscape, necessitating innovative tools and solutions.