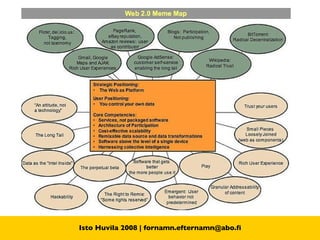
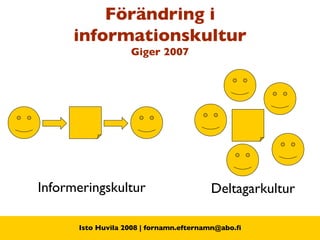
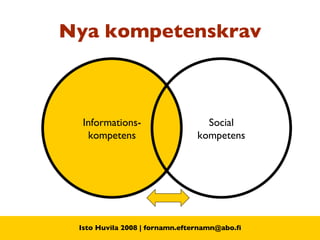
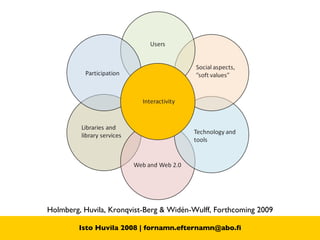
The document discusses the concept of Library 2.0 and how it relates to Web 2.0. Library 2.0 refers to a set of library services designed to meet user needs influenced by Web 2.0, focusing on making libraries more interactive, collaborative, and community-driven. It aims to empower users and break down barriers to information. Key aspects include user-generated content, social networking features, and facilitating participation and knowledge-sharing between library users and staff.